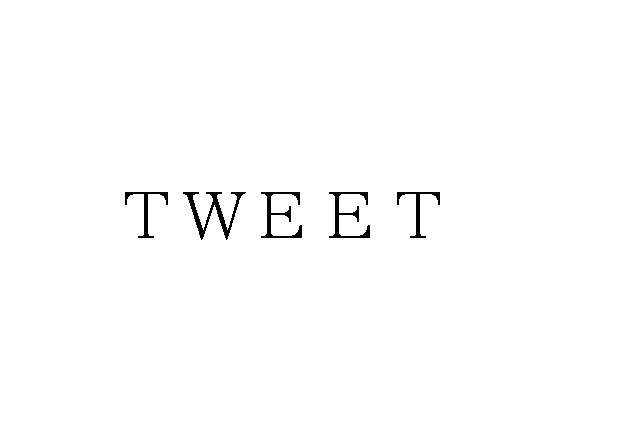The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed a trademark opposition claimed by fashion company Esprit against trademark registration no. 6155147 for a work mark consisting of “ESPRIT” and “SELECTION” over retail service in class 35 by finding dissimilarity and less likelihood of confusion with “ESPRIT”.
[Opposition case no. 2019-900260, Gazette issued date: July 31, 2020]
“ESPRIT SELECTION”
Opposed mark, a wordmark consisting of “ESPRIT” with larger font size and “SELECTION” with smaller font size in two lines (see below), was filed by a Japanese business entity, Harmonick Co., Ltd., on November 19, 2018, by designating ‘retail services or wholesale services for a variety of goods in each field of clothing, foods and beverages, and living ware, carrying all goods together’ in class 35.

Applicant commercially provides gift catalogs bearing the opposed mark so that shoppers can find a great selection of products from the catalogs.
The JPO admitted registration on June 21, 2019, and published for opposition on July 16, 2019.
Opposition by ESPRIT
To oppose registration within a statutory period of two months counting from the publication date, Esprit International filed an opposition on September 11, 2019.
In the opposition, Esprit asserted the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) and (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law because of a high degree of popularity and reputation of owned senior trademark registrations nos. 2097119 and 2187153 for the “ESPRIT” logo (see below) as an international fashion brand and close resemblance with the opposed mark “ESPRIT SELECTION”.
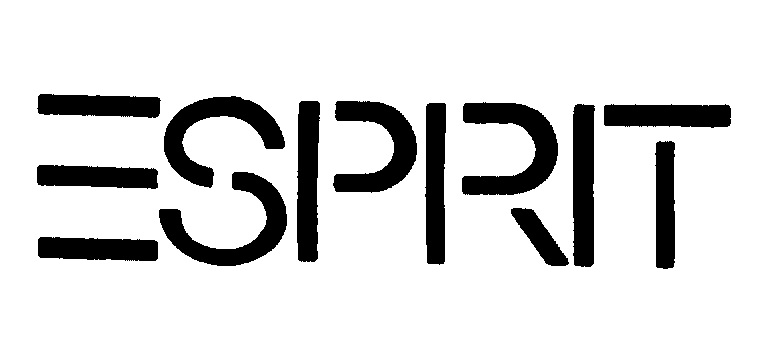
Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entities ’ well-known goods or services, to the benefit of brand owners and consumers.
Article 4(1)(xix) prohibits registering a trademark that is identical with, or similar to, other entity’s famous mark, if such trademark is aimed for unfair purposes, e.g. gaining unfair profits, or causing damage to the entity.
Esprit argued the term “SELECTION” is descriptive in relation to the retail service in question since it is commonly used to indicate ‘the things chosen or selected’ or ‘an assortment of things from which a choice can be made’. If so, relevant consumers would conceive the term “ESPRIT” as a prominent portion of the opposed mark and thus both marks shall be unquestionably deemed similar as a whole.
Besides, the service in question is closely related to the opponent business since Esprit offers affordable fashion and lifestyle with a huge selection of ladies’, men’s, and kids’ clothing as well as accessories.
Board Decision
The Opposition Board of JPO denied a high degree of popularity and reputation of “ESPRIT”, stating that the opponent failed to produce evidence to demonstrate actual and substantial use of the opponent mark, advertisement, sales record, and market share in Japan. A mere fact that opponent is a global company doing business in more than 40 countries and operates more than 440 “ESPRIT” shops in European and neighboring Asian countries are insufficient and irrelevant to find whether the opponent mark becomes famous among relevant consumers and traders in Japan.
Besides, the term “SELECTION” shall not be taken to explicitly indicate the quality of the service in question. Even if it is depicted with smaller font size than “ESPRIT”, the Board would not find a reasonable ground to believe the term “ESPRIT” solely plays a role of source indicator in the configuration of the opposed mark. If so, the opposed mark shall be assessed in its entirety.
Based on the foregoing, the Board concluded “ESPRIT SELECTION” and “ESPRIT” are dissimilar as a whole from visual, phonetical, and conceptual points of view. Provided that the opponent mark has not acquired a certain degree of reputation and popularity among relevant consumers in Japan, it unlikely happens that the consumers confuse or misconceive a source of the opposed mark with Esprit or any entity systematically or economically connected with the opponent. Thus, the opposed mark shall not be canceled on the grounds of Article 4(1)(xv) and (xix).