On October 12, 2023, the Japan IP High Court affirmed the JPO refusal decision to TM App no. 2021-93231 for word mark “athlete Chiffon” in class 43 due to a lack of distinctiveness.
[Court case no. Reiwa5(Gyo-ke)10038]JPO refusal decision
Disputed mark, consisting of two words “athlete” and “Chiffon” in standard character, was filed for use of providing temporary accommodation; accommodation bureaux services; providing foods and beverages in class 43 with The Japan Patent Office (JPO) on July 27, 2021 (TM App no. 2021-93231).

The JPO examiner rejected the mark based on Article 3(1)(iii) and Article 4(1)(xvi) of the Japan Trademark Law by stating that relevant consumers at sight of the disputed mark would merely conceive of a restaurant to provide Chiffon cakes for athletes and it will cause misrepresentation of a particular quality of service when used on other services.
Applicant filed an appeal against the examiner’s rejection. However, the JPO Appeal Board sustained the examiner’s findings and decided to refuse the disputed mark on March 22, 2023.
Appeal to the IP High Court
On April 20, 2023, the applicant filed a lawsuit to dispute registrability of the disputed mark with the IP High Court and asked the court to annul the JPO decision based on the facts that the JPO has allowed registration of lots of trademarks containing the term “athlete”, but none of them restrict its usage of designated goods or services “for athletes”. Cake shops containing a term “Chiffon” in their trade name have even delt with cakes other than chiffon. If so, the JPO obviously made an error in denying distinctiveness of respective term “athlete” and “Chiffon”. Because of it, the JPO refusal decision shall be cancelled.
IP High Court decision
From the produced evidence, the IP High Court found that, in the industry of foods and beverages, terms such as “athlete cake” and “athlete pan cakes” are commonly used to indicate special goods and service for athletes. If so, relevant consumers and traders would consider a term consisting of “athlete” followed by generic word of goods or service as an indication to specify the target of the goods or service (for athletes). “Chiffon” is known in the industry as a term to indicate ‘food that is made light by adding the clear part of eggs that have been beaten’ and commonly used in conjunction with other descriptive term, e.g., “Choco chiffon”, “banana chiffon”, “Valentine chiffon”.
Under the circumstances, the court has a reason to believe that relevant consumers would consider the term “athlete Chiffon” as a mere descriptive indication of the restaurant to provide chiffon (cakes) for athletes when used in relation to the service in question.
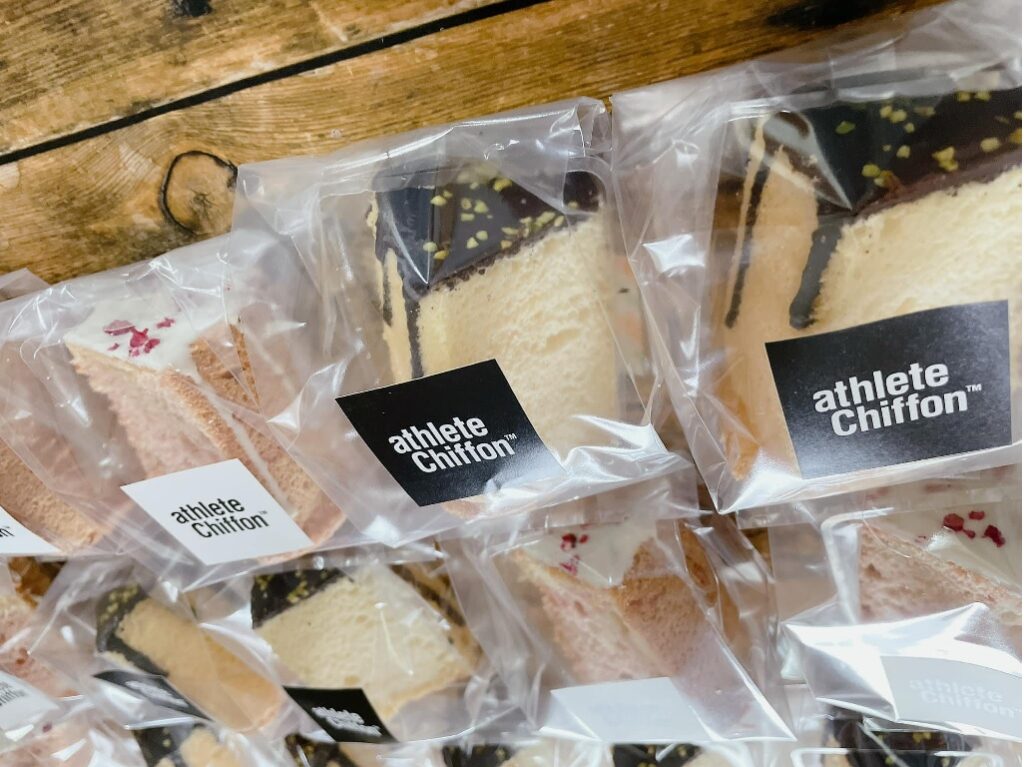

A fact that several cake shops containing a term “Chiffon” in their trade name have delt with cakes other than chiffon is irrelevant to the case given the consumers conceive of chiffon cake at sight of the term “athlete Chiffon” when used on restaurant service.
Based on the foregoing, the court held the JPO did not make any error in finding facts and applying trademark law and thus the disputed mark shall be unregistrable under Article 3(1)(iii) and 4(1)(xvi).