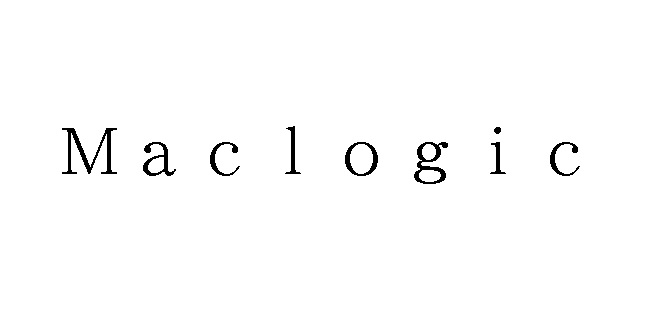On May 1, 2023, the Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition filed by Apple Inc. against TM Reg no. 6536066 for the wordmark “HiTune” by finding dissimilarity to and an unlikelihood of confusion with “iTunes”.
[Opposition case no. 2022-900242]Opposed mark
UGREEN GROUP LIMITED, a Chinese company, filed the wordmark “HiTune” (see below) for use on computer peripheral devices, data processors, earphones, headphones, microphones, sound transmitting apparatus, and other goods in class 9 with the JPO on November 10, 2021.

The mark was registered on March 29, 2022, without receiving any refusal in the course of the substantive examination taken place by the JPO.
UGREEN has promoted wireless stereo earphones/earbuds bearing the mark.

Opposition by Apple Inc.
On June 6, 2022, Apple Inc. filed an opposition to “HiTune” and contended that the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(xi) and (xv) of the Japan Trademark Law by citing earlier trademark registration nos. 4570713 “iTUNE”, 4610312 “ITUNES”, 5155781 “iTunes”, IR943547 “ITUNES” in class 9.

Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit the registration of a junior mark that is identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entities’ well-known goods or services.
Apple Inc. argued that the mark “iTunes” has been famous as a source indicator of the opponent in relation to application software and multi-content distribution service. In view of the remarkable similarity between “HiTune” and “iTunes” by representing the second letter “i” in lower case and the third letter “T” in upper case, relevant consumers would associate the opposed mark with the opponent when used on goods of class 9 in question.
JPO decision
To my surprise, the JPO Opposition Board admitted a certain level of recognition of the mark “iTunes” as a source indicator of Apple Inc. in connection with application software enabling to download music or movies and to manage the contents among consumers of music distribution service, however, denied a substantial level of reputation and popularity of the opponent mark due to a lack of objective evidence produced to the Board.
In assessing the similarity of marks, the Board stated:
Differences such as the presence or absence of “H” at the beginning of the word, the difference between upper- and lower-case letters, and the presence or absence of “s” at the end of the word have a significant impact on the overall visual impression of both marks, which consist of relatively short letters. Therefore, the marks are clearly distinguishable from appearance.
There are distinctions between the sound “ha” and “a” at the beginning of a word, and the presence or absence of the sound “z” at the end of a word. These differences have a material effect on overall sounds given the relatively short sound structure. Therefore, there is less risk of mishearing each other when pronounced.
Since both marks do not give rise to any specific meanings, there is no room to cause confusion in concept.
If so, the Board has a reason to believe both marks are distinctively dissimilar.
Bearing in mind the Board finds that the opponent mark “iTunes” has not become famous among relevant consumers in Japan and has a low degree of similarity to the opposed mark “HiTune”, it is unlikely that the consumers confuse or misunderstand a source of goods in question bearing the opposed mark with Apple Inc. from the totality of the circumstances.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO decided the opposed mark shall not be canceled and dismissed the opposition entirely.