The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed a trademark opposition claimed by social media giant, Twitter, Inc. against trademark registration no. 6138010 for word mark “TWEET” in class 33 by finding the TWEET mark is relatively unknown as a source indicator of Twitter Inc.
[Opposition case no. 2019-900193, Gazette issued date: April 24, 2020]
Opposed mark
A wordmark “TWEET” in standard character was filed by a Japanese sake brewery, Shirataki Sake on June 21, 2018, over Japanese sake [Nihonsyu]; sake, distilled rice spirits; sake substitute; Japanese white liquor [Shochu]; Japanese sweet rice-based mixed liquor [Shiro-zake]; Naoshi [Japanese liquor]; Japanese Shochu-based mixed liquor [Mirin]; western liquors; alcoholic fruit beverages; Japanese Shochu-based beverages [Chuhai]; Chinese liquors; flavored liquors in class 33, and published for opposition on May 14, 2019, after registration on April 12, 2019.
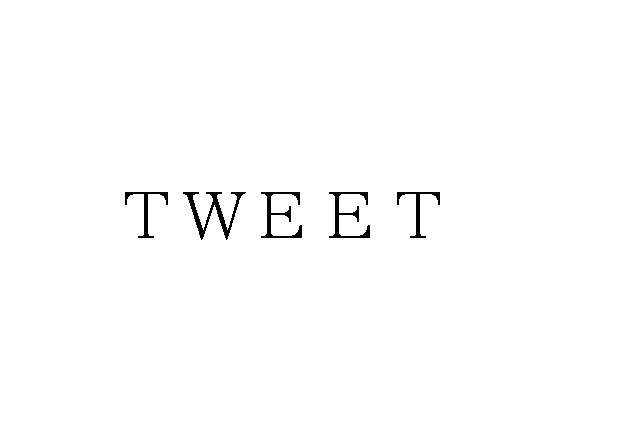
Opposition by Twitter, Inc.
On July 12, 2019, US social media giant, Twitter, Inc. filed an opposition and argued opposed mark shall be revocable in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) and (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law due to a likelihood of confusion with, or identical with its famous “TWEET” mark registered in various classes other than 33.
Article 4(1)(xv)
Article 4(1)(xv) prohibits registering a trademark which is likely to cause confusion with the business of other entities.
Twitter is a ‘microblogging’ system that allows users to send and receive short posts called “tweets”. Tweets can be up to 140 characters long and can include links to relevant websites and resources. The Japanese version of Twitter was launched in 2008 and its MAU (monthly active users) has been increasing since. Compared to the American population, 35.7% of Japanese actively use Twitter actively while only 20.7% of Americans actively use Twitter. Now, 17% of Twitter’s worldwide revenue comes from the Japanese market.
Twitter, Inc. argued that the above facts suggest “TWEET” has acquired substantial reputation and popularity among the general public in Japan as a source indicator of the opponent.
Even though goods in dispute are remotely associated with SNS services, a lot of alcoholic consumers have obviously made use of Twitter and “tweet” since major breweries advertise their goods on Twitter so frequently and gain a substantial number of followers on Twitter.

If so, relevant consumers of goods in dispute are likely to misconceive the source of goods bearing opposed mark with Twitter, Inc., or any entity systematically or economically connected with the opponent.
Board Decision
The Opposition Board admitted a remarkable degree of reputation and popularity of opponent trademark “Twitter” in connection with a real-time communication service based on the produced evidence boasting more than 45 million MAU in Japan as of December 2018.
Meanwhile, the Board questioned if “TWEET” has been used as a source indicator of opponent business since the evidence shows the term has been used to indicate function or usage of Twitter in a descriptive manner. Consequently, the Board found “TWEET” is relatively unknown as a source indicator of Twitter Inc.
Based on the foregoing, the Board decided opposed mark shall not be revocable in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) and (xix) since it is unlikely that relevant consumers conceive of the opponent or connect the alcoholic beverages bearing opposed mark “TWEET” with Twitter.