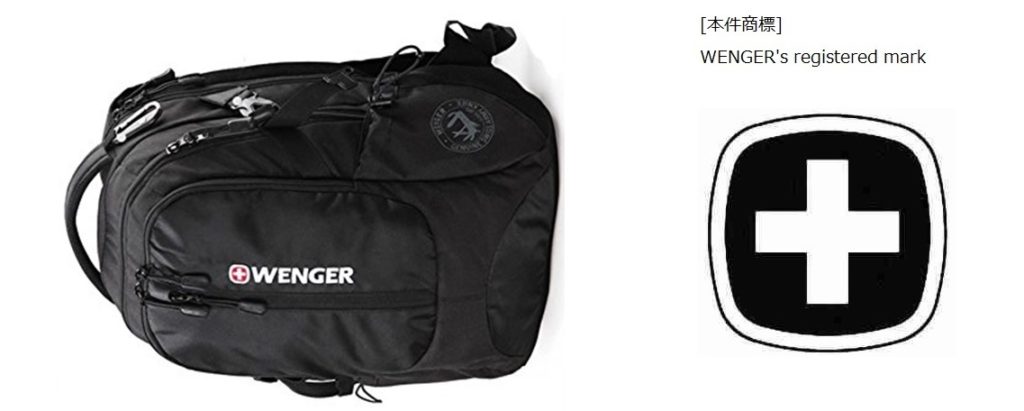
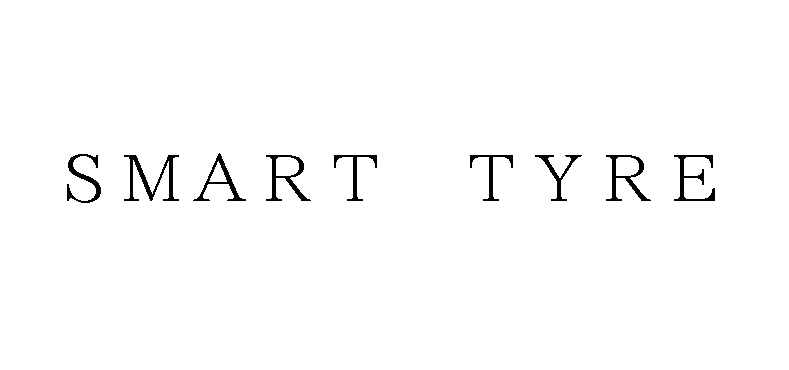On April 21, 2021, the Japan IP High Court affirmed the Tokyo District Court’s decision in favor of Wenger S.A. and ruled to dismiss the appeal brought by TravelPlus International who was sentenced for trademark infringement by using cross design marks similar to the Wegner cross on backpacks. [Court case nos. IP High Court Reiwa2(ne)10060]
WENGER
Wenger, the Swiss company, has owned international registration no. 1002196 for the cross mark (see below) for use on backpacks of class 18 and others goods in Japan since November 5, 2010.

SWISSWIN
TravelPlus International (TI) distributed “SWISSWIN” brand backpacks adorned with a logo evoking the Swiss flag which consists of a cross surrounded by a square in Japan. According to the court decision, an affiliated company of TI has produced the Wenger bags as an OEM vendor.

IP High Court ruling
The IP High Court dismissed the appeal entirely and issued a decision addressing the interpretation of similar marks evoking the Swiss flag that is unregistrable under the Trademark Law.
1. Evaluation of color difference on cross design
TI argued color difference shall be a crucial factor in this case based on Article 4(1)(iv) of the Japan Trademark Law that prohibits registration of an identical or similar mark to the Red Cross.
However, the judge denied the allegation by stating that any cross design dissimilar to the Red Cross can be registrable under the article. If so, it does not make sense to find the color difference on cross designs that would materially affect the similarity of the marks. Both marks should be assessed in their entirety by taking account of other elements as well.
2. Assessing figurative element except for cross design
TI argued both marks should be assessed similarly on the assumption that the square plays a dominant role of source indicator based on Article 4(1)(i). Any mark identical or similar to a foreign national flag is unregistrable under the article. If so, it should not be allowed to claim trademark infringement based on the cross design which is undoubtedly similar to the Swiss flag.
However, the judge dismissed the allegation and reiterated its stance that in finding similarity of the mark, both marks should be assessed in their entirety, not only with the square but also the cross, since both marks just consist of these elements.