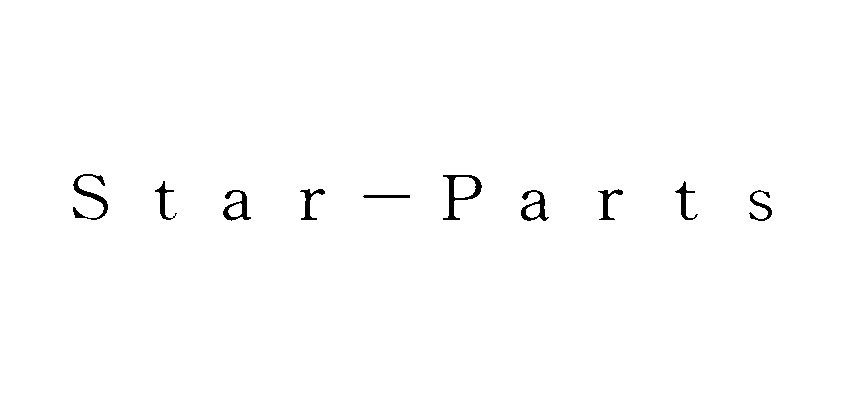Colombian Coffee Federation (FNC) failed a fight for invalidation of Japanese TM Registration no. 5901554 for word mark “EMERALD” in class 30 owned by The Coca-Cola Company, one of the world’s largest beverage company in the US.
[Invalidation case no. 2018-890017, Gazette issued date: August 28, 2020]
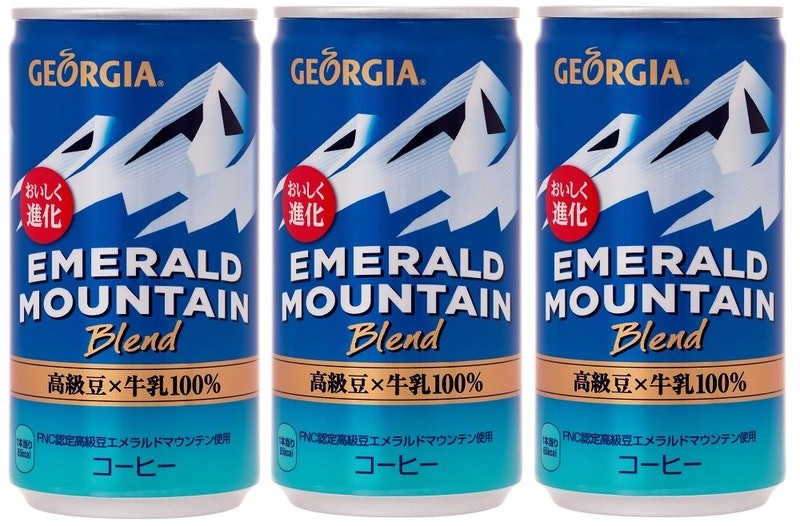
EMERALD MOUNTAIN
Emerald Mountain is a top brand name of Colombian coffee approved by FNC (NGO organization, the union of coffee producer established in 1927 joining over 560,000 members for enhancing quality, production, and export) guaranteed hand-picked and hand-screened beans of which quantity is only 3 –1% of the total production of Colombia coffee beans.
The FNC owns several trademark registrations for “EMERALD MOUNTAIN” in Japan.
In the early 90s, Emerald Mountain began to be sold by Coca-Cola as canned liquid coffee under the Georgia brand in thousands of vending machines across Japan. Since 1997 it has become the most sold coffee in Japanese history as well as the #1 beverage sold by Coca-Cola in Japan. Every can of Georgia Emerald Mountain coffee has an explanation of the Colombian origin of the coffee as well as the high-quality certification of the FNCS. With annual sales of more than 630 million cans, Georgia Emerald Mountain Blend is undoubtedly Emerald Mountain’s leading product within the Japanese market.
EMERALD
Irrespective of a long-standing relationship, The Coca Cola Company, in 2011, sought registration for a wordmark “EMERALD” over artificial coffee, coffee-based beverages, prepared coffee and cocoa, tea, ice in class 30 which confronted with a severe objection from FNC.
FNC was successful in removing the registration
by means of a non-use cancellation in 2017. However, The Coca Cola Company deliberately
filed a new trademark application for the same mark in 2015 immediately when the
registered mark was vulnerable for cancellation on grounds of non-use. The JPO
allowed registration of the new application in December 2016.
To contend, FNC filed an invalidation
action against the EMERALD mark in March 2018.
Invalidation petition by FNC
FNC argued the EMERALD mark shall be invalidated in contravention of Article 4(1)(vii), (x), (xi), (xv), and (xix) of the Trademark Law by stating that “EMERALD MOUNTAIN” has acquired substantial reputation and popularity as an indicator of high-quality Columbian coffee as a result of continuous sales promotion in Japan since 1970. In the coffee industry, coffee beans grown in highland are often named with the term “MOUNTAIN”, e.g. “BLUE MOUNTAIN”, “CRYSTAL MOUNTAIN”, “CARRIBERAN MOUNTAIN”, “CORAL MOUNTAIN”. In this respect, “EMERALD” shall play a prominent role in “EMERALD MOUNTAIN”. If so, both marks are deemed similar and it is likely that relevant consumers confuse or associate artificial coffee, coffee-based beverages, prepared coffee and cocoa, tea, ice bearing the EMERALD mark with “EMERALD MOUNTAIN”.
Besides, The Coca Cola Company has been using “EMERALD MOUNTAIN” on canned-liquid coffee under license from FNC. Presumably, the disputed mark was filed in anticipation of non-use cancellation claimed by FNC. In the cancellation proceeding, The Coca-Cola Company did neither answer nor respond. These facts clearly show the disputed mark was filed just to avoid cancellation even if The Coca-Cola Company had no intention to use it. It is really annoyance and free-riding on the famous marks with a fraudulent intention.
JPO decision
From the totality of evidence and circumstances, the JPO admitted a high degree of reputation and popularity of EMERALD MOUNTAIN as a source indicator of FNC’s high-quality Columbian coffee beans. In the meantime, the JPO questioned if relevant consumers connect the term “EMERALD” with FNC when used on coffee since the evidence did not disclose EMERALD MOUNTAIN is actually abbreviated to “EMERALD” in commerce. Likewise, it is suspicious whether “BLUE MOUNTAIN”, “CRYSTAL MOUNTAIN”, “CARRIBERAN MOUNTAIN”, “CORAL MOUNTAIN” are recognized with its short name, namely, “BLUE”, “CRYSTAL”, “CARRIBEAN”, “CORAL”.
In assessing the similarity of the mark, the JPO found “EMERALD MOUNTAIN” and “EMERALD” are dissimilar from visual, phonetic, and conceptual points of view. Given both marks are distinctively dissimilar, it is unlikely to find a likelihood of confusion in connection with the goods in dispute.
Even if The Coca-Cola Company filed the disputed mark with an intention to avoid the non-use cancellation, it would be anything but punishable in view of dissimilarity between marks. Besides, from the produced evidence, the JPO was unable to find fraudulent intention by Coca Cola to be blamed for invalidation.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO decided to dismiss
the invalidation action.