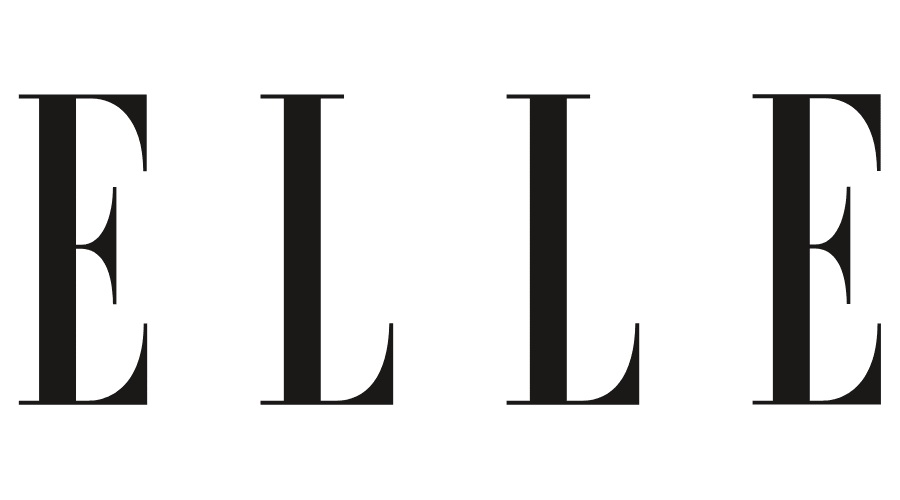In a trademark opposition disputing the similarity and the likelihood of confusion between “Olympic” and “Olimple”, the JPO did not side with the IOC (International Olympic Committee).
[Opposition case no. 2021-900173]
Olimple
The opposed mark, consisting of the term “Olimple” written in the alphabet and the Japanese katakana character (see below), was applied with the Japan Patent Office (JPO) on January 28, 2020, for use on facial skin care gel, cosmetics, soaps, and other goods in class 3 by Olimple Co., Ltd.

The JPO granted protection on February 2, 2021, and published for opposition on March 9, 2021.
The applicant promotes medicated skin care gel for men bearing the Olimple mark.

Opposition by IOC
Opponent, IOC claimed the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(vi), (vii), (xi) and (xv) of the Japan Trademark Law by citing earlier International Registration no. 1128501 for wordmark “OLYMPIC” covering various goods and services in class 3 and other classes.
IOC argued a close resemblance between “OLYMPIC” and “Olimple” by stating:
- Both marks share four of the seven letters. Besides, the two letters at the end of the word, “le” and “IC” looks similar.
- The third letters “I” and “Y” of both marks are pronounced as “li” accompanied by the second letter “L”.
- Being that consumers are accustomed to several terms with a prefix of “OLYMP”, e.g., “OLYMPISM”, “OLYMPIAN” in connection with “OLYMPIC”, they will see the literal element “Olimp” as a dominant portion of the opposed mark.
- If so, relevant consumers are likely to confuse the opposed mark with “OLYMPIC” when used on goods in question.
JPO decision
The JPO did not question the famousness of the OLYMPIC mark as a source indicator of the IOC. However, the Opposition Board negated the similarity between “Olimple” and “OLYMPIC” on the following grounds.
- The term “Olimple” shall be deemed as a coined word because it is not a word that appeared in a language dictionary and does not give rise to any specific meaning in relation to the goods in question.
- There is a remarkable difference in the presence or absence of Japanese katakana characters. In addition to the difference between upper- and lower-case letters after the second letter, there are distinctions in the third letter “i” and “Y”, the sixth letter “l” and “I”, and the letters “e” and “C” at the end. In the configuration of the relatively short seven-letter alphabet, both marks are sufficiently distinguishable by appearance.
- Phonetically, both marks are unlikely to cause confusion as a whole because of a clear difference in the fourth and fifth sounds.
- It is obvious that both marks are dissimilar in concept.
The Board did not find a reason to believe relevant consumers would misconceive the source of the opposed mark merely because of close attention to the literal portion of “OLYMP” and “Olimp”, and its similarity.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO dismissed the entire allegations and decided on July 13, 2022, that the opposed mark shall remain valid as the status quo.