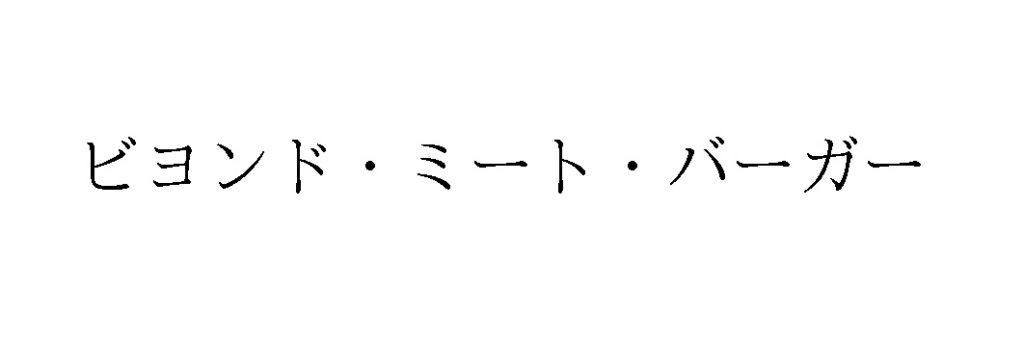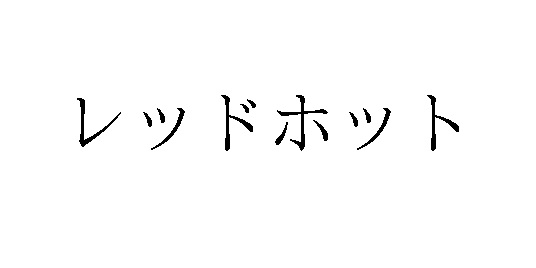In a recent administrative decision, the Japan Patent Office (JPO) found the word mark “Virtual Marathon” lacks distinctiveness in relation to marathon races of class 41 although the JPO admitted registration of the word mark “Virtual Tokyo Marathon” in the same class.
[Appeal case no. 2022-001910, Decision date: December 12, 2022]Virtual Marathon
During the COVID-19 pandemic when large gathering in person is not possible, many major running decided to go virtual around the globe.
On March 30, 2020, R-bies Co., Ltd., a Japanese company managing sports events and sports media, filed a word mark “Virtual Marathon” written in Japanese Katakana characters (see below) for use on various goods and services including marathon races in classes 9, 41, and 42.

Virtual Tokyo Marathon
Three months later, Tokyo Marathon Foundation filed a trademark application for the word mark “Virtual Tokyo Marathon” in standard character on various goods and services in classes 9, 35, 36, 38, 41, 42, and 45.

The JPO did not raise any objection to the Virtual Tokyo Marathon mark and granted protection on June 21, 2021.
Examiner’s Refusal
In the meantime, on April 7, 2021, the JPO examiner raised her objection to the Virtual Marathon mark due to a lack of inherent distinctiveness in relation to sports events and marathon races of class 41 by stating that the term “virtual marathon” is commonly used to indicate an organized event where participants run a full marathon in an individual place of their choice during a specific date range tracked on an app on their smartphones. If so, the mark “Virtual Marathon” shall not meet the requirements of Article 3(1)(iii) of the Japan Trademark Law. The applicant filed a written response and argued the distinctiveness of the mark, however, the examiner did not withdraw her objection and decided to reject the entire application on November 8, 2021.
R-bies Co., Ltd. filed an appeal to the refusal on February 8, 2022, and argued the inherent distinctiveness of the Virtual Marathon mark by citing a junior trademark application for the “Virtual Tokyo Marathon” mark that was considered distinctive in relation to the same goods and services (TM Reg no. 6420795).
JPO decision
The JPO Appeal Board affirmed the examiner’s findings by citing a lot of web articles pertinent to virtual marathon races organized in Japan.
Under the circumstance, the Board has a reason to believe that relevant consumers at the sight of the Virtual Marathon mark are likely to conceive of online footrace in which each participant goes out and runs the full marathon in their own time, not as a source indicator of sports event managed by R-bies Co., Ltd. or other specific entity.
Based on the foregoing, the Appeal Board upheld the examiner’s refusal and decided to reject the word mark “Virtual Marathon” in contravention of Article 3(1)(iii).
As a matter of interpretation of the Trademark Law, provided that “Virtual Marathon” is to be rejected under Article 3(1)(iii), “Virtual Tokyo Marathon” shall be rejected on the same ground as well unless Tokyo Marathon Foundation demonstrates acquired distinctiveness of the mark as a result of substantial use. I believe it is impossible because the Tokyo Marathon was never virtually started before registration.