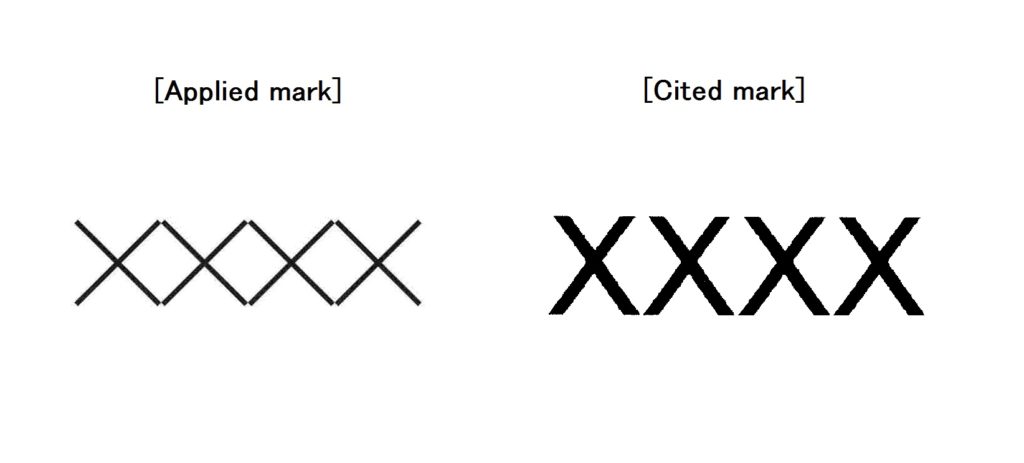On July 3, 2019, the Japan IP High Court reversed a decision of the Japan Patent Office (JPO) finding that the company Daimler AG was entitled to registration of “EQ” for Motor vehicles in class 12, even though the term “EQ” by itself is descriptive for the goods.
[Case no. Heisei31(Gyo-ke)10004, Daimler AG vs the JPO Commissioner]
The EQ Application
The JPO has refused registration to an application for EQ in standard characters (word only, see below) on the basis that the mark was descriptive for the goods “Motor vehicles” in class 12 based on Article 3(1)(v) of the Trademark Law.

The article prohibits an applied mark from registering if it consists solely of a very simple and common mark. Trademark Examination Guidelines (TEG) stipulates that a mark consisting of one or two alphabetical letters is not eligible for registration under the article. Click here.
A mark consisting of two alphabetical letters is not capable of identifying the source of the goods due to a lack of distinctiveness because a combination of two alphabetical letters is limited on quantity and currently used to represent a model name of vehicle, e.g. BMW XS, TOYOTA Carina ED, Ferrari FX, Nissan GT-R.
Descriptive terms falling under the article are only capable for registration based on Article 3(2) if they have “acquired distinctiveness”, which means the term has taken on a meaning in the public view so that people see the term as a trademark identifying the goods rather than simply describing the goods.
In this regard, Daimler AG argued the EQ mark, a coined term originating from “Electric Intelligence” to appeal design, extraordinary driving pleasure, high levels of everyday suitability and maximum safety of electric car by Mercedes-Benz, has acquired distinctiveness since launching the brand at the Paris Motor Show in September 2016.

JPO Decision
However, the JPO dismissed the argument on the grounds that:
- Daimler has neither used the EQ mark by itself as a name of electric car nor produced evidences of its plan to sell electric car named “EQ”.
- Daimler uses the EQ mark in a stylized design in press releases. If so, it is questionable whether relevant consumers conceive the EQ mark in standard characters as a source indicator of Mercedes-Benz.
- According to the produced evidences, Daimler uses the EQ mark in combination with other literal elements, e.g. “Generation EQ Concept”, “Concept EQA”, “EQC”, “smart vision EQ for two”, “EQ POWER”, “EQ POWER+”.
- There are no actual domestic sales of the electric car using the applied mark during the past two years from the date Daimler launched the brand in fact.
- A combination of two alphabetical letters, “E” and “Q”, has been generally used as a mode name in association with vehicles, e.g. TOYOTA electric car “eQ”, HYUNDAI luxury sedan “EQ900”, Zhengzhou Nissan truck “EQ1060”, Laufenn tyre “S FIT EQ”, ALPINE car navigation “EX11Z-EQ”, SPECIALLIZED bicycle “ALIBI SPORT EQ”. If so, the EQ term shall not be eligible for monopoly by a specific entity any longer.
The Appeal Board of JPO also upheld the refusal.
[Appeal case no. 2018-650016]
To contest the administrative decision, Daimler AG filed an appeal to the IP High Court on January 15, 2019.
IP High Court Ruling
The court first found the EQ mark in standard characters is not eligible for registration under Article 3(1)(v) of the Trademark Law.
In the meantime, the court found Daimler has newly released, promoted, and used the EQ mark with a combination of “POWER” as a new brand concept of electric car by Mercedes-Benz. Given a space for single letter between “EQ” and “POWER”, relevant consumers at the sight of promotional materials, advertisements and car magazines pertinent to Mercedes-Benz’s new electric car brand would perceive “EQ” as a specific source indicator. Taking account of enormous number of circulation of magazines (approx. 230,000) and advertisements for users (170,000 per year), the court held the EQ mark has been well known for a source indicator of Daimler electric car among relevant consumers and traders even if the duration of actual use and sales amount are not sufficient by themselves.
Notably, the court also negated fact-finding by JPO regarding ordinary use of the term EQ in association with vehicles by stating that since competitors use the term in a tight combination with other literal elements, they can be simply perceived as a mode name. If so, such use shall not be construed to negate acquired distinctiveness of the EQ mark by Daimler.
Based on the foregoing, the court ruled the EQ mark is entitled to trademark registration based on Article 3(2) of the Trademark Law and reversed a decision by the JPO on that account.