On February 28, 2022, the Appeal Board of Japan Patent Office (JPO) reversed the examiner’s rejection and decided to register the applied mark “COCOGOLF” in classes 25 and 28 by finding dissimilarity to Chanel’s earlier registration for the mark “COCO.”
COCOGOLF
The applied mark consists of the word “COCOGOLF” (see below).
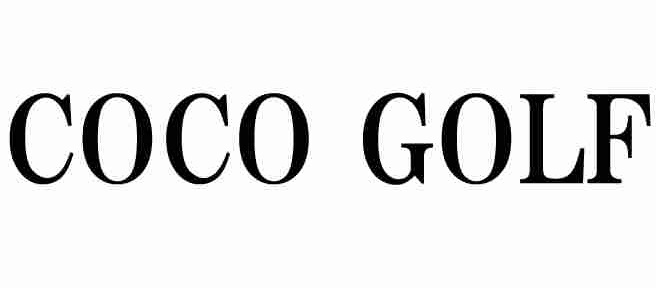
Applicant, E-COME GROUP Co., Ltd., filed it for use on various goods in classes 18, 25, and 28 on November 27, 2022. [TM Application no. 2020-146448]
Confronting office action from the JPO, the applicant divided the application and filed a new trademark application on goods of ‘sports shoes; sportswear’ in class 25 and ‘golf bags; golf equipment in class 28 on July 2, 2021. [TM Application no. 2021-82743]
The JPO examiner rejected the mark in contravention of Article 4(1)(xi) of the Japan Trademark Law on October 12, 2021.
The examiner cited earlier trademark registration nos. #6169514 (cl. 25, 35) and IR699469 (cl. 25) for the wordmark “COCO” owned by Chanel SARL, and found the applied mark “COCOGOLF” is confusingly similar to the cited mark “COCO” when used on the designated goods in class 25 and 28.
The applicant filed an appeal against the rejection on November 17, 2021, and argued for the dissimilarity in the marks.
JPO Decision
The Appeal Board found the applied mark shall be assessed in its entirety by stating:
- Visually, there is no reason to consider the term “COCO” as a prominent portion of the applied mark because of its configuration.
- The applied mark gives rise to the pronunciation of ‘coco-golf’. The whole sound can be pronounced easily in a breach.
- The Board has no reason to believe the term “GOLF” perse has been used to represent specific goods in relation to the goods in question.
- If so, relevant consumers at the sight of sports shoes, sportswear, golf bags, and golf equipment bearing the applied mark would see it as a whole, and are unlikely to consider the term “COCO” as a prominent source indicator of the applied mark.
Based on the foregoing, the Board found the examiner erred in finding “COCO” to be separable from “GOLF.” Consequently, the Board held the applied mark is dissimilar to the mark “COCO” and granted “COCOGOLF” registration.
[Appeal case no. 2021-15790]