On June 7, 2022, the Appeal Board of the Japan Patent Office (JPO) decided to reject a red color mark used on the soles of high heels by Christian Louboutin due to a lack of inherent and acquired distinctiveness.
[Appeal case no. 2019-29921]Louboutin’s Red Soles
Fast on the heels of the introduction to register color marks in Japan, Christian Louboutin filed a trademark application for a color mark consisting of a red (Pantone 18-1663TP) colored in soles (see below) for use on high heels in class 25 on April 1, 2015 (TM App no. 2015-29921).
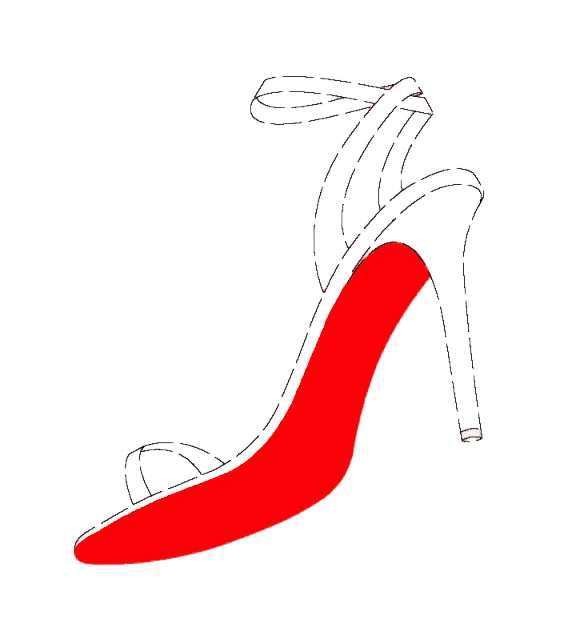

The JPO examiner refused the color mark based on Article 3(1)(iii) of the Japan Trademark Law by stating red color has been commonly used on shoes to enhance the aesthetic appearance and attract consumers of high heels. Red-colored heels and shoes have been widely distributed before the launch of Louboutin shoes in 1996 in Japan and even now. Under the circumstance and trade practice, the examiner had no reason to believe the color mark perse has acquired distinctiveness as a source indicator of Louboutin among relevant consumers in Japan. If so, the mark shall not be registrable under Article 3(2).
Louboutin filed an appeal against the refusal and disputed the inherent and acquired distinctiveness of Louboutin’s red soles as a color mark on October 29, 2019.
To bolster the acquired distinctiveness of the red soles, Louboutin conducted an online brand awareness survey to target 3,149 females, aging from 20 to 50 and having a domicile in Tokyo, Osaka, or Nagoya where Louboutin have stores. The survey demonstrated that 43.35% of the interviewees conceived of Louboutin in the answer to an unaided open-ended question (Q1). 53.99% associated the color mark with Louboutin in the answer to a closed-ended question, where it mentioned Louboutin along with other close competitors (Q2). Louboutin argued, that from the survey, it is obvious that Louboutin’s red soles have acquired distinctiveness among relevant consumers and shall be registered under Article 3(2) even though lacking inherent distinctiveness.
JPO Appeal Board decision
The Appeal Board affirmed the examiner’s findings and found the color mark perse lacks distinctiveness in relation to the goods in question by taking into account of fact that a lot of shoes with red-colored soles have been distributed by other shoemakers in Japan.
In the assessment of acquired distinctiveness, the Board pointed out a fact that more than half of the interviewees who live in the region where Louboutin stores are could not conceive of Louboutin in the answer to Q1. The survey was insufficient to admit acquired distinctiveness of the applied mark among relevant consumers nationwide, the Board found.
Even among the consumers who could associate the color mark with Louboutin, the Board had an opinion that as a matter of fact, they will be unable to distinguish Louboutin high heels from competitors’ shoes simply by means of red-colored soles without the aid of another source indicator, a wordmark “Louboutin”, used on the shoes given a lot of red-soled heels and shoes have been distributed by competitors as follows.
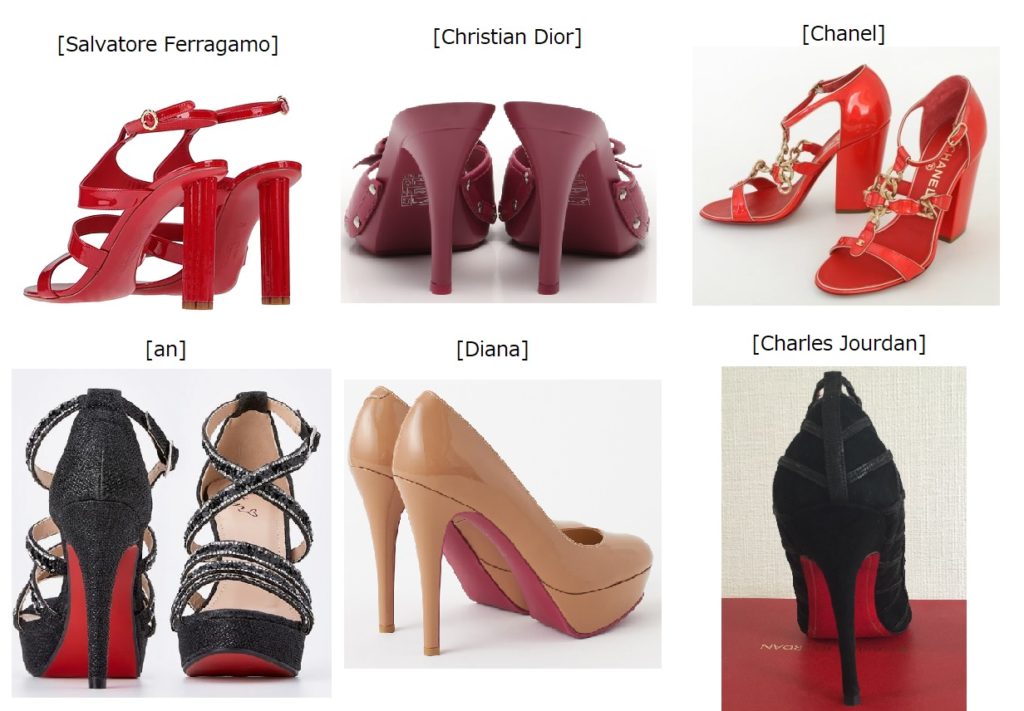

Besides, under the current trade practice, the Board considered it will inevitably cause a severe disorder and excessive restriction to competitors if it allows registration of a red color that has been freely used in the relevant industry to enhance the aesthetic appearance of shoes.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO concluded the color mark shall not be registrable under Article 3(2) as well.