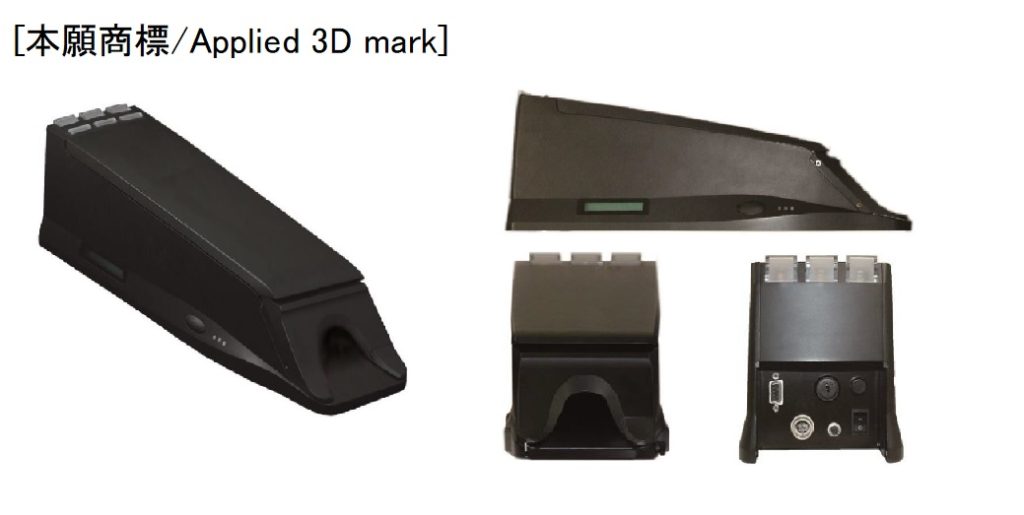
The Japan IP High Court, in its ruling on November 29, 2018, did not side with Paramount Bed Co., Ltd., a Japanese manufacturer and distributor of medical and nursing care product, who filed an appeal against refusal decision by JPO to TM Application no. 2015-29155 for 3D mark representing the shape of home care bed.
[Case No. Heisei 30 (Gyo-ke) 10060]
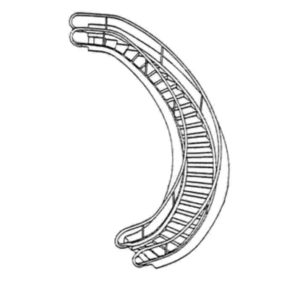
3D shape of home care bed
Disputed mark, representing three-dimensional shape of nursing care bed, was filed on March 31, 2015 by designating nursing care bed and mattress in class 20. The Japan Patent Office (JPO) refused the mark due to a lack of distinctiveness.



Paramount Bed argued acquired distinctiveness as a source indicator of Paramount nursing care bed through substantial use of the mark and its unique shape.
According to the argument, Paramount has distributed more than 145,000 sets of nursing care bed and mattress which 3D shape is identical with the applied mark. The company spent USD 2,400,000 to advertise the bed in newspaper and USD 20,000,000 in TV commercial during the past five years. Paramount produced on-line questionnaire results which showed more than 60 % of relevant traders have recognized the shape as a series of Paramount Bed.
IP High Court ruling
The IP High Court dismissed the allegation entirely, stating that the produced evidences are unpersuasive to conclude the 3D shape acquired distinctiveness as a source indicator of Paramount Bed’s business because of below-mentioned reasons.
- As long as nursing care beds are likely to be used by general public, questionnaire results answered by traders are insufficient to demonstrate acquired distinctiveness among relevant consumers.
- Given the shape of applied mark occasionally appears while nursing care bed is in operation and the bed has coverlet on it in ordinary days, it is questionable whether relevant consumers have perceived the shape of applied mark per se as a source indicator.
- Besides, catalogs and advertisements pertinent to Paramount nursing care bed show configurations of the bed other than the shape of applied mark.
Based on the foregoing, the court upheld JPO decision.