On 23 June 2020, the Japan IP High Court decided a case concerning a single color mark that was rejected for registration by the Appeal Board of the Japan Patent Office (“JPO”).
Single Color Mark
On 1 April 2015, Hitachi Construction Machinery (“Hitachi”) filed an application for trademark registration with JPO consisting of a single color per se, namely orange (Munsell: 0.5YR5.6/11.2) over the goods of hydraulic excavators, wheel loaders, road loaders, loaders [earch moving machines] in class 7, and rigid dump trucks in class 12 (TM Application no. 2015-29999).

By the decision of 19 September 2019, the Appeal Board of JPO declared the applied color mark to be refused in contravention of Article 3(1)(iii) and Article 3(2) of the Trademark Law, finding that the graphic representation of the color mark constituted the “mere single orange color, without contours”. If so, the mark is not inherently distinctive and it is lacking acquired distinctiveness. In the course of the appeal trial, Hitachi amended and restricted the designated goods to “hydraulic excavators”.
Article 3(2) is a provision to allow registration of any mark with which the relevant public will associate a particular source, manufacturer, or producer over time through the trademark owner’s usage.
On 30 October 2019, Hitachi appealed against the JPO decision.
IP High Court decision
At the outset, the court stated it is inevitable on the case concerning single color mark to take the interest of competitors who deal with the goods in question into consideration since allowing one trader to exclusively use this color would likely to cause unjust competitive practice in form of monopolistic power of use in favor of one trader only.
From the produced evidence, Hitachi has allegedly used the color in question on hydraulic excavators and other construction machines since 1974.
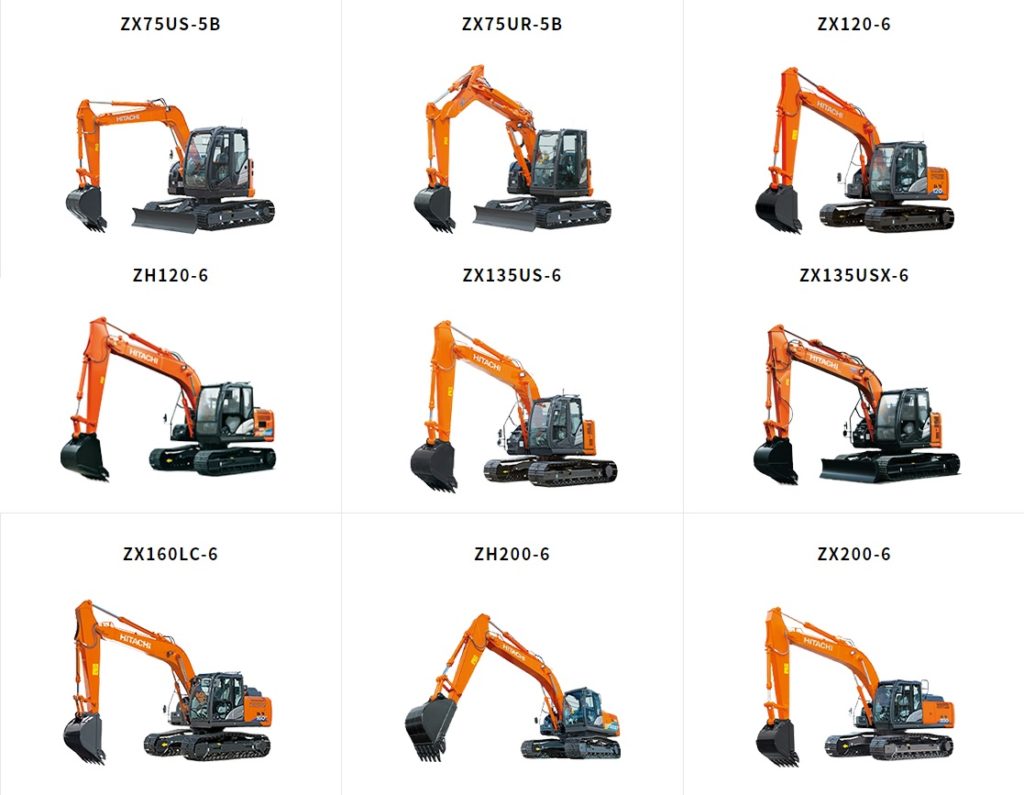

Hitachi consecutively holds a 20% market share (14.6%) of hydraulic excavators over the past four decades in Japan. The research showed that approx. 95.9 % (185 out of 193) of traders in the construction industry were able to associate the color with Hitachi.
In the meantime, several competitors use similar color on hydraulic excavators
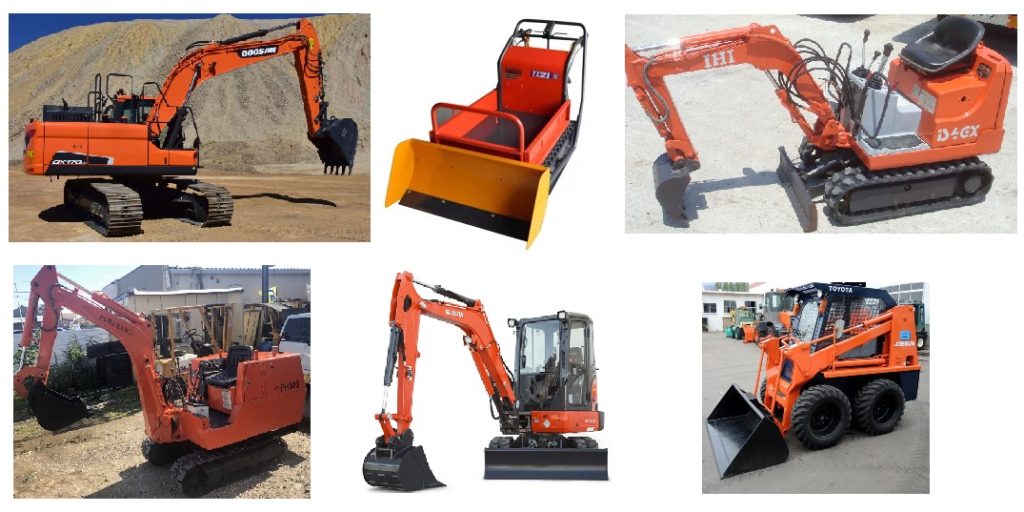

In the decision, the court found orange color is one of the colors commonly seen in our daily life. Besides, the Japan Industrial Standard (JIS) adopts orange as a safety sign-color aiming to prevent harm to the human body and damage to properties. Because of it, at construction sites, we often see several items colored in orange, e.g. helmets, rain suits, guard fens, work clothes, tower cranes, construction vehicles.
Hitachi Hydraulic Excavators have other colors, in fact, namely, a house mark “HITACHI” colored in white, buckets (attachments), cockpits, and crawlers colored in black. If so, the applied mark shall be capable of playing the role of source indicator in combination with these. Thus, the court would not find reasonable grounds to believe that the orange color per se acquired distinctiveness as a source indicator of Hitachi’s Hydraulic Excavators.
The court even suspected credibility of the research by finding that it narrowly targeted traders or consumers who own more than 10 hydraulic excavators, precisely it showed 36.8% in light of initial research number of targets, 502 persons, and the questionnaire ‘Please answer. What maker do you think hydraulic excavator is?” was insufficient to conclude acquired distinctiveness since its answer may simply suggest one of the colors of Hitachi’s Hydraulic Excavators.
Even if hydraulic excavators market in Japan is an oligopoly with five makers accounting for 90 % of the industry share, and the orange color has been consecutively used by Hitachi only, it does not mean every competitor agreed to refrain from using the color given orange has been used on various goods in the construction and agriculture industry in general.
Based on the foregoing, the court affirmed the JPO decision and dismissed Hitachi’s allegations in contravention of Article 3(1)(iii) and 3(2).
Click here to see the court decision in Japanese.
Thus, it is obvious that a very high standard of distinctiveness needs to be attached to a single-color mark if the same has to be claimed for trademark protection.
This case was a second court decision concerning a single color mark.
The first case, Reiwa1(Gyo-ke)10119 ruled on March 11, 2020, also ended with the rejection of a single orange color mark in contravention of other ground, Article 3(1)(vi).
How JPO Examines Color Marks
As of now (12 July 2020), 543 color marks were applied for registration with JPO since the commencement of the Non-Traditional trademark application in April 2015.
So far, only 8 marks are successfully registered. See below.
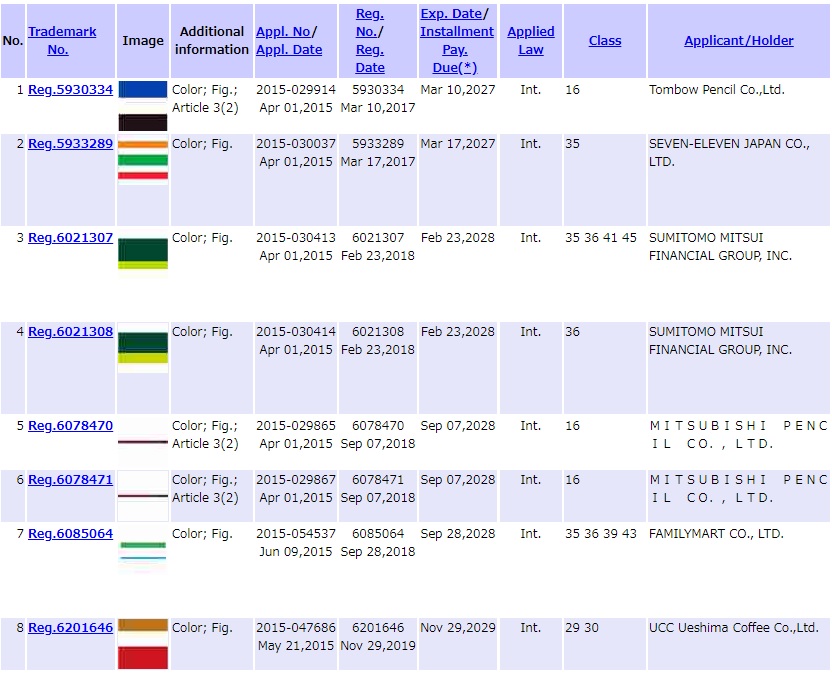
In sum, the registration rate of color mark is barely 1.5%!
It is noteworthy none of a ‘single’ color mark has been granted to registration.