In a decision to the invalidation trial jointly claimed by INSTITUT NATIONAL DE L’ORIGINE ET DE LA QUALITE and CONSEIL INTERPROFESSIONNEL DU VIN DE BORDEAUX, the Invalidation Board of Japan Patent Office (JPO) ordered to invalidate TM registration no. 5737079 for a word mark “Bord’or” in script fonts (see below) in violation of Article 4(1)(vii) of the Trademark Law.
[Invalidation case no. 2016-890075]

TM Registration no. 5737079
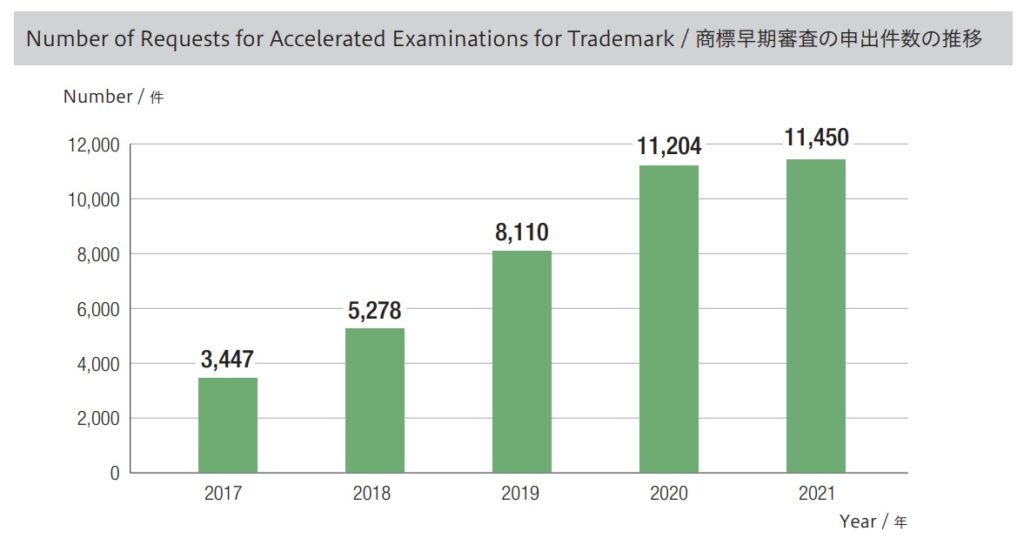
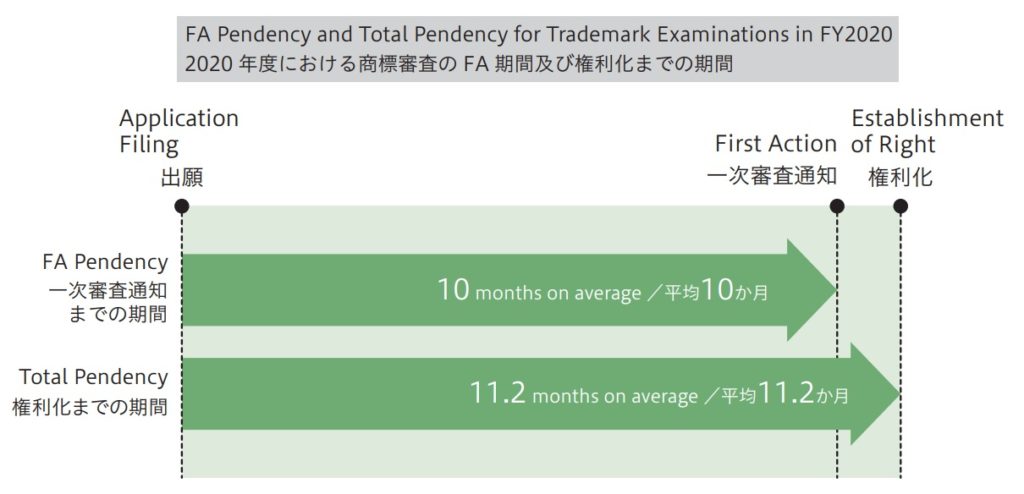
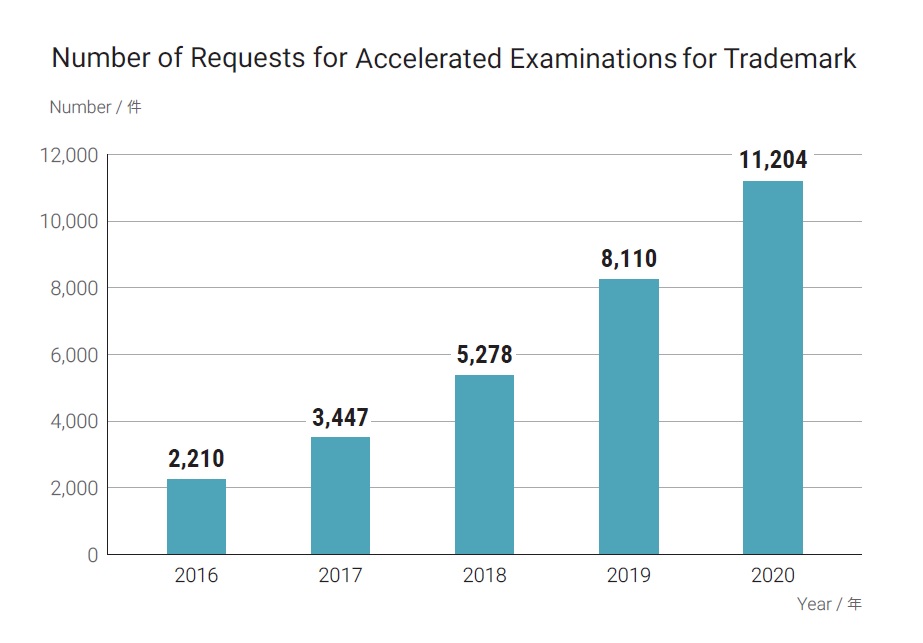
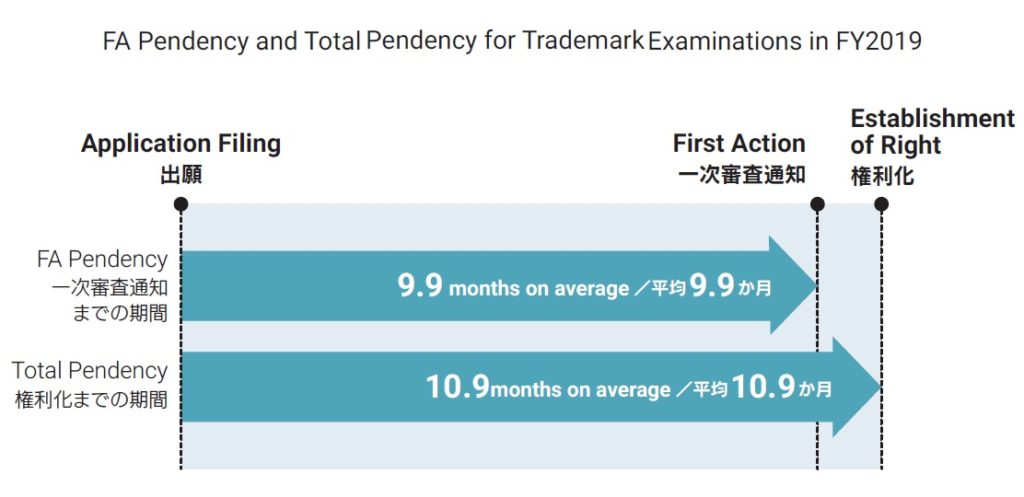
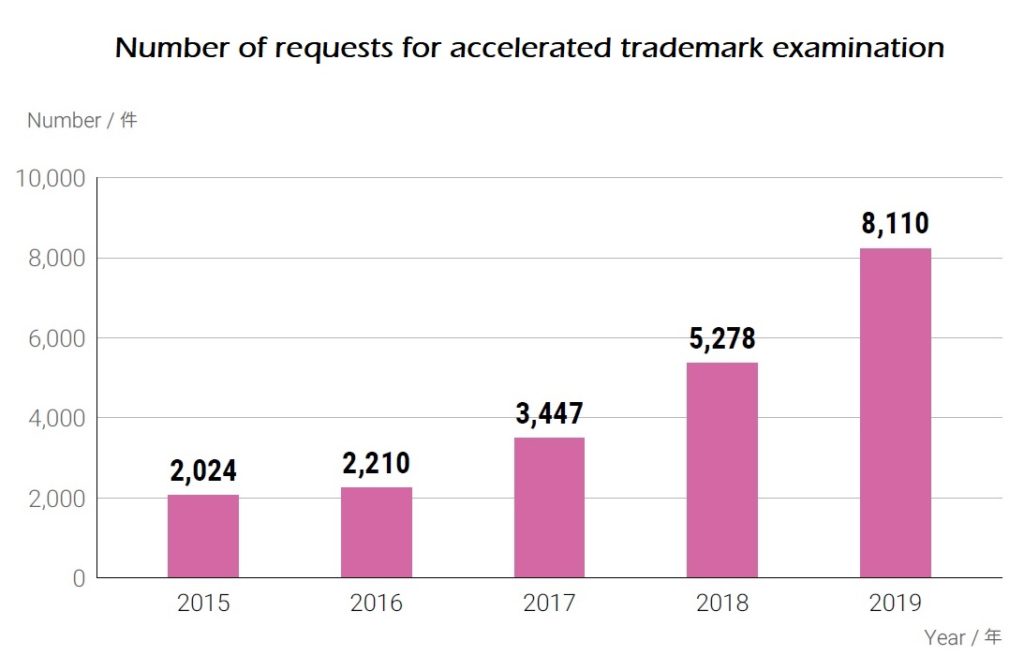
Mark in dispute (see above), owned by a Japanese legal entity, was filed on October 9, 2014 by designating various types of alcoholic beverages including wines in class 33. After an initial application, applicant requested the JPO to expedite substantive examination. In accordance with the request, JPO examiner put a priority on the mark and admitted to grant registration in three months subsequent to substantive examination.
Accelerated Examination
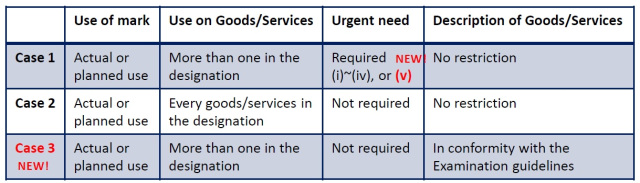
JPO applies the accelerated examination system to trademark application on the condition that the application meets the following condition.
- Applicant/licensee uses or will use applied mark on one of designated goods/services at least, and there exists an urgency to registration, e.g. unauthorized use by third parties, basic application to international registration,
- All designated goods/services are actually or shortly used by applicant/licensee, or
- Applicant/licensee uses or will use applied mark on one of designated goods/services at least, and all the goods/services are designated in accordance with a standard description based on Examination Guidelines for Similar Goods and Services.
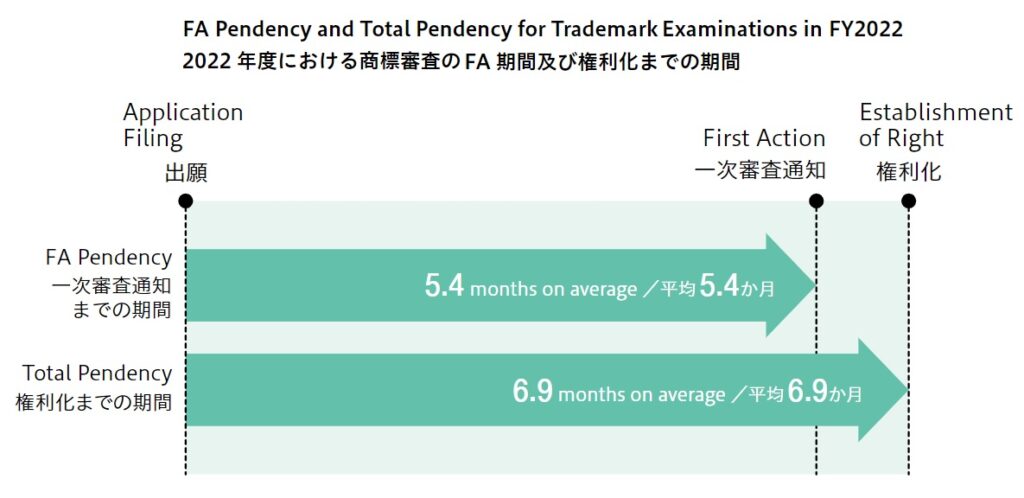
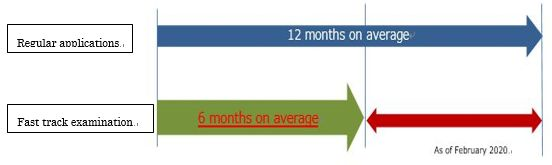
Accelerated examination system enables applicant to obtain examination results in less than two months on average, which is four months shorter than regular examination.
Claimants’ allegation
Claimants argued disputed mark gives rise to the same pronunciation with BORDEAUX, “ bɔːˈdəʊ”. If so, relevant consumers shall conceive BORDEAUX, a world-famous geographical name known for an origin of French wine. Besides, according to the document produced by applicant to demonstrate actual use of disputed mark on designated goods in requesting accelerated examination, it evidently reveals intention to free-ride or dilute fame of prestigious wine.
Thus, if disputed mark is used on wines originated from areas other than BORDEAUX, it severely does harm to fame and aura of prestigious wine constituted under the strict control of domicile of origin. Then, inevitably it causes disorder to a world of global commerce in a manner inconsistent with international fidelity.
To bolster the allegation, claimants cited precedent trademark decisions involving famous French wine, e.g. ROMANEE-CONTI, BEAUJOLAIS NOUVEAU, CHABLIS. Inter alia, IP High Court ruled a word mark “CHAMPAGNE TOWER” invalid in relation to “CHAMPAGNE” based on Article 4(1)(vii).
Article 4(1)(vii) of the Japan Trademark Law
Article 4(1)(vii) prohibits any mark likely to offend public order and morals from registering.
Trademark Examination Guidelines sets forth criteria for the article and samples.
- Trademarks that are “likely to cause damage to public order or morality” are, for example, the trademarks that fall under the cases prescribed in (1) to (5) below.
(1) Trademarks which are, in composition per se, characters or figures, signs, three-dimensional shapes or colors or any combination thereof, or sounds that are unethical, obscene, discriminative, outrageous, or unpleasant to people. It is judged whether characters, figures, signs, three-dimensional shapes or colors or any combination thereof, or sounds are unethical, discriminative or unpleasant to people, with consideration given to their historical backgrounds, social impacts, etc. from a comprehensive viewpoint.
(2) Trademarks which do not have the composition per se as prescribed in (1) above but are liable to conflict with the public interests of the society or contravene the generally-accepted sense of morality if used for the designated goods or designated services.
(3) Trademarks with their use prohibited by other laws.
(4) Trademarks liable to dishonor a specific country or its people or trademarks generally considered contrary to the international faith.
(5) Trademarks whose registration is contrary to the order predetermined under the Trademark Act and is utterly unacceptable for lack of social reasonableness in the background to the filing of an application for trademark registration.
- Examples that fall under this item
(i) Trademarks that contain characters such as “university” and are likely to be mistaken for the name of universities, etc. under the School Education Act.
(ii) Trademarks that contain characters such as “士(shi)” which are likely to mislead that they represent national qualifications.
(iii) Trademarks of the name of a well-known or famous historical personage which are determined to have the risk of taking a free ride on public measures related to that personage and damage the public interests by inhibiting the performance of such measures.
(iv) Trademarks with figures indicated in a manner that may impair the dignity and honor of national flags (including foreign national flags)
(v) A sound mark related to the services of “medical treatment” which causes people to recognize siren sounds generated by ambulances that are well known in Japan.
(vi) A sound mark which causes people to recognize national anthems of Japan and other countries.
Board decision
Board found in favor of claimants that “BORDEAUX” has acquired a high degree of popularity and reputation among Japanese consumers as a source indicator of wines originated from the Bordeaux district. As long as disputed mark gives rise to the same pronunciation with BORDEAUX, it is undeniable that consumers are likely to connect the disputed mark with BORDEAUX wine or its district. If so, disputed mark free-rides or dilutes lure and image of BORDEAUX wine, and adversely affects domicile of origin strictly controlled by French government.
Consequently, Board decided to invalidate Bord’or in violation to Article 4(1)(vii).
Protection of geographical indication
The Japan Trademark Law contains provisions to protect geographical indication.
In principle, a mark merely consisting of geographical name or location is deemed descriptive and falls under Article 3(1)(iii). Even if a mark is combined geographical indication with other distinctive elements, it is subject to Article 4(1)(xvi) since the mark may mislead the quality when used on goods from other areas.
Regarding a mark indicating a place of origin off wine, Article 4(1)(xvii) plays a significant role.
Article 4(1)(xvii)
No trademark shall be registered if the trademark is comprised of a mark indicating a place of origin of wines or spirits of Japan which has been designated by the Commissioner of the Patent Office, or a mark indicating a place of origin of wines or spirits of a member of the World Trade Organization which is prohibited by the said member from being used on wines or spirits not originating from the region of the said member, if such a trademark is used in connection with wines or spirits not originating from the region in Japan or of the said member.
Geographical indications to be protected under the article can be reviewed by accessing http://www.jpo.go.jp/tetuzuki_e/t_tokkyo_e/pdf/appendix2.pdf
In this regard, it should be noted that Article 4(1)(xvii) is applicable to any mark containing a term to represent protected GI in itself. In other words, Article 4(1)(xvii) can’t block “Bord’or” since disputed mark does not contain “BORDEAUX” or its transliteration.