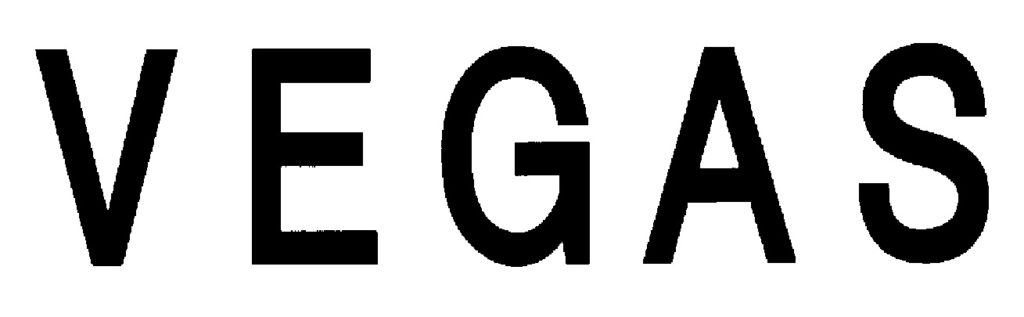On May 20, 2020, the Japan IP High Court denied the JPO decision and sided with Apple Inc. by finding the “CORE ML” mark is dissimilar to senior trademark registration no. 5611369 for word mark “CORE” in connection with computer software of class 9.
[Case no. Reiwa1(Gyo-ke)10151]
CORE ML
Apple Inc. filed a trademark application for word mark “CORE ML” in standard character by designating computer software in class 9 on November 6, 2017 (TM App no. 2017-145606).
Apple’s Core ML is its own framework for Machine Learning used across Apple products for performing fast prediction or inference with easy integration of pre-trained machine learning models on the edge, which allows you to perform real-time predictions of live images or video on the device.
JPO decision
The Japan Patent Office (JPO) rejected “CORE ML” in contravention of Article 4(1)(xi) of the Trademark Law due to a conflict with senior trademark registration no. 5611369 for word mark “CORE” in standard character over electronic machines, computer software, and other goods in class 9 owned by Seiko Holdings Corporation.
Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit from registering a junior mark that is deemed identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
In the decision, the JPO stated applied mark apparently consists of two words, “CORE” and “ML”. The term “CORE”, a familiar English word meaning ‘a central and foundational part’, would play a role of source indicator in connection with the goods in question. In the meantime, “ML” is a descriptive term since it is commonly used as an abbreviation of ‘Machine Learning’ in the computer software industry. If so, it is permissible to select the term “CORE” as a dominant portion of applied mark and compare it with the cited mark “CORE”.
To contend against the decision, Apple Inc. filed an appeal to the IP High Court.
IP High Court ruling
The IP High Court, at the outset, referred to the Supreme Court ruling in 2008 which established the criterion to grasp a composite mark in its entirety in the assessment of similarity of the mark.
“Where a mark in dispute is recognized as a composite mark consisting of two elements or more, it is not permissible to assess the similarity of mark simply by means of taking out an element of the composite mark and then comparing such element with the other mark, unless consumers or traders are likely to perceive the element as a dominant portion indicating its source of origin of goods/service, or remaining elements truly lack inherent distinctiveness as a source indicator in view of sound and concept.”
Based on the criteria, the court found that applied mark shall be assessed in its entirety on the following grounds:
- “CORE” would be merely recognized as a term to mean ‘a central and foundational part’ in connection with goods in question.
- It is unlikely that relevant consumers at the sight of “CORE ML” used on computer software conceive the term “ML” as an abbreviation of ‘machine learning’. If so, “ML” would not give rise to any specific meaning.
- The above facts suggest that “CORE” would never play a dominant role and “ML” shall not be considered less distinctive than “CORE” as a source indicator in view of the concept.
- From appearance and sound, there is no reasonable ground to believe “CORE” and “ML” shall be recognized individual and separable.
Based on the foregoing, the court pointed out the JPO erred in finding applied mark appropriately and decided that the applied mark “CORE ML” is deemed dissimilar to the cited mark “CORE” as a whole given the remarkable difference in sound and appearance, even if both marks resemble in concept.