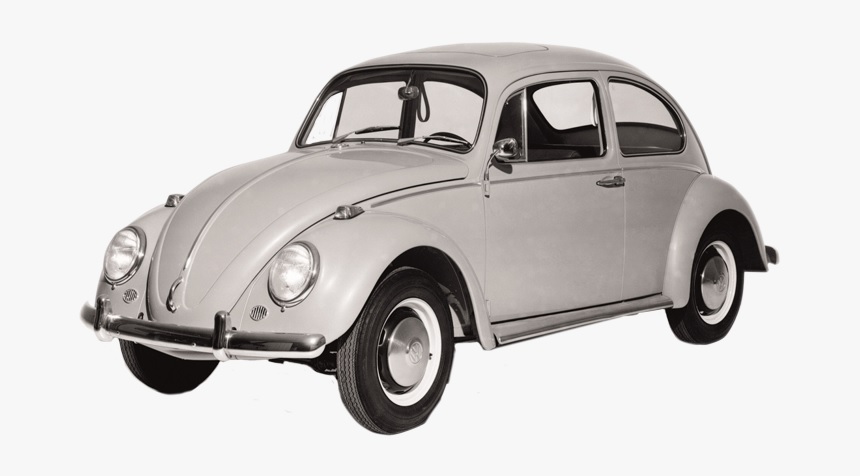
In an attempt to register TM App no. 2020-1611 for 3D mark representing a bottle shape of the SK-II Facial Moisturizing Lotions, the Japan Patent Office (JPO) upheld the examiner’s rejection and dismissed the appeal filed by The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G).
[Appeal case no. 2022-6, decided on May 9, 2024]
SK-II
P&G filed a trademark application for 3D bottle shape of the SK-II cosmetic lotions (see below) in class 3 with the JPO on February 14, 2020 (TM App no. 2020-1611).

SK-II is a Japanese-based multinational beauty brand with premium skincare solutions sold in East Asia, North America, Europe, and Australia, launched in the early 1980s.

Allegedly, domestic sales of the “SK-II” facial treatment essence (moisturizing lotions) contained in the applied 3D mark were approximately JPY 10 billion to 16.5 billion in each of the fiscal years from 2016 to 2020.
Article 3(1)(iii)
The JPO examiner rejected the 3D mark based on Article 3(1)(iii) of the Japan Trademark Law due to a lack of inherent distinctiveness.
Article 3(1)(iii) is a provision to prohibit registration of any mark that is descriptive in relation to designated goods and service. Trademark Examination Guideline (TEG) refers to 3D bottle shape of goods as an example subject to the article.
Where trademark is merely recognized as the shapes of designated goods (including shape of packages), it is evaluated just to indicate the “shape” of the goods. Moreover, the same principle shall apply to cases where a trademark is recognized as part of the shapes of designated goods (including their packages).
Article 3(2)
P&G argued acquired distinctiveness of the 3D mark as a result of substantial use. However, the examiner rejected the argument, stating that since the applied mark has been consistently used with the word mark “SK-II” on every bottle, there is no reason to believe that the 3D shape perse has played a role in identifying the source of the cosmetics.
Therefore, the applied mark shall not be registrable based on Article 3(2) of the Trademark Law due to a lack of acquired distinctiveness.
JPO decision
The JPO Appeal Board found the applied mark should be rejected in accordance with Article 3(1)(iii) due to the prevalence of cylindrical bottles in the contexts of cosmetics and other industries.
In its decision, the Board noted that a considerable amount of sales had been made to date and that advertising and promotional activities had been conducted at a considerable expense. The SK-II cosmetics bearing the 3D mark have been extensively advertised through a variety of channels, including magazine advertisements, TV commercials, events, and other campaign activities. They have also been widely covered by the web media and other media outlets.
In the meantime, the Board pointed out the use of distinctive words, such as “SK-II”, “SECRET KEY II”, “MAX FACTOR” etc., on the bottle of the CK-II facial moisturizing lotions. In this respect, there is no sufficient evidence and material featuring the 3D mark so that consumers at the sight of advertisements can consider the bottle shape as a source indicator.
Besides, P&G did not produce evidence of brand awareness survey to demonstrate acquired distinctiveness of the bottle shape. The registration of the same mark in other jurisdictions, such as the United Arab Emirates and South Korea, does not have any binding power in Japan when it comes to evaluating distinctiveness.
Based on the above findings, the Board concluded that the 3D mark per se has not acquired distinctiveness and should not apply Article 3(2).