The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an appeal filed by a Japanese individual who sought registration for use of the wordmark “AIR NECKTIE” on neckties in class 25 due to the similarity to NIKE “AIR.”
[Appeal case no. 2020-4106, Gazette issued date: February 26, 2021.]
AIR NECKTIE
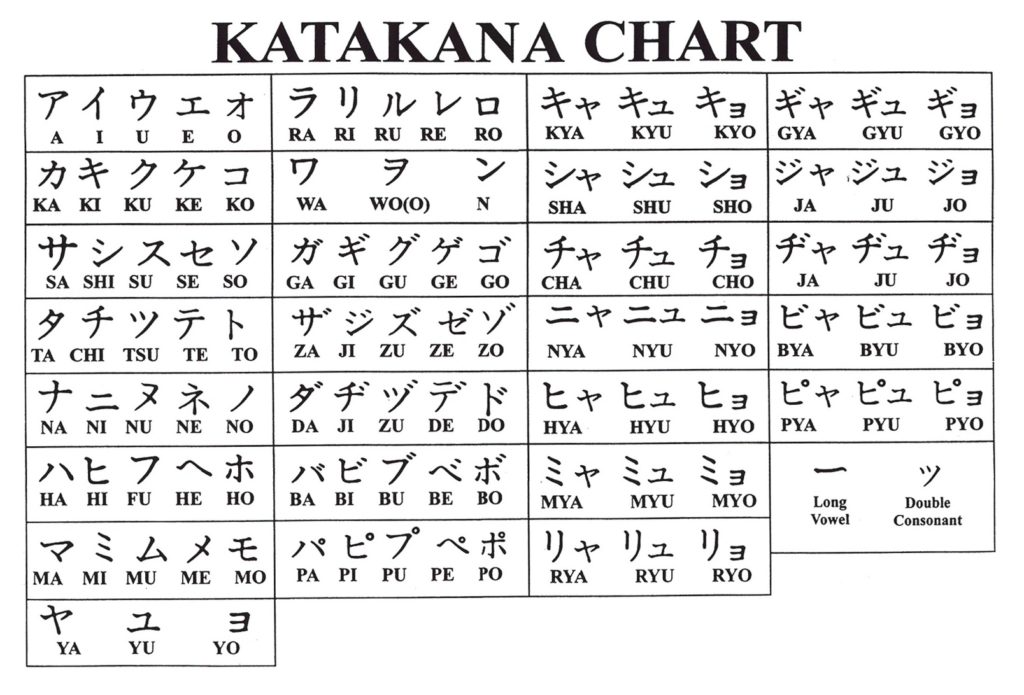
The mark in question, consisting of two English words “AIR” and “NECKTIE”, and its transliteration in a Japanese katakana character (see below), was filed for use on ‘neckties’ in class 25 with the JPO on July 6, 2018 [TM Application no. 2018-88482].

AIR
The examiner raised her objection based on Article 4(1)(xi) of the Trademark Law by citing senior registration nos. 502137 and 4327964 for the mark “AIR” owned by NIKE Innovate C.V. (see below) which cover clothing, shoes, neckties, and other goods in class 25.
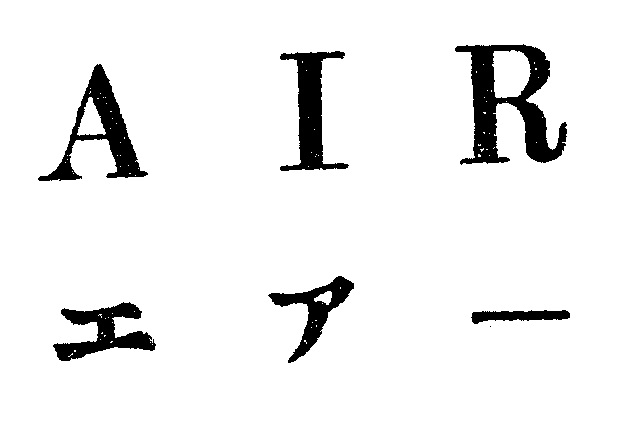
Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit registering a junior mark that is deemed identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
Regardless of the arguments made on a written response to the office action by the applicant, the JPO examiner entirely rejected the “AIR NECKTIE” mark based on the ground.
On March 6, 2020, the applicant filed an appeal against the refusal with the JPO and disputed that the applied mark “AIR NECKTIE” is dissimilar to the cited mark “AIR.”
JPO decision
The JPO Appeal Board referred to the tests established by the Supreme Court ruling in 2008 to determine whether it is permissible to take out respective elements of the composite mark when assessing the similarity of two marks.
“Where a mark in dispute is recognized as a composite mark consisting of two elements or more, it is not permissible to assess the similarity of marks simply by means of taking out an element of the composite mark and then comparing such element with the other mark, unless consumers or traders are likely to perceive the element as a dominant portion indicating its source of origin of goods/service, or remaining elements truly lack inherent distinctiveness as a source indicator in view of sound and concept.”
Based on the tests, the Board found that it is permissible to take out a literal element “AIR” from the applied mark and compare it with the citations by stating the following grounds:
- The applied mark can be seen as a composite mark consisting of ‘AIR’ and ‘NECKTIE’ because of the space between two words.
- “NECKTIE” is unquestionably recognized as a generic term in connection with ‘neckties’ in class 25.
- Relevant consumers at the sight of neckties bearing the mark “AIR NECKTIE” would conceive the term “AIR” as a prominent source indicator.
- “AIR NECKTIE” does not give rise to any specific meaning in its entirety.
- The above facts suggest that “NECKTIE” lacks inherent distinctiveness in relation to the goods in question, and it would not play the role of source indicator of the applied mark in view of sound as well as concept.
Based on the foregoing, the Board affirmed the examiner’s rejection and decided that the applied mark “AIR NECKTIE” is similar to the cited marks as a whole given the remarkable similarity in sound and concept, even if the word “NECKTIE” differentiates two marks in appearance.