The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition filed by Samsung, the world’s largest smartphone maker, against TM Reg no. 6263685 for wordmark “Funky Galaxy” by stating the opposed mark would not cause confusion with Samsung “Galaxy” even when used on smartphones.
[Opposition case no. 2020-900229, Gazette issued date: November 11, 2021]Opposed mark
On April 12, 2019, KING Entertainment Co., Ltd. applied for registration of wordmark “Funky Galaxy” in standard character for use on goods and services in classes 9, 16, 35, and 41. The goods in class 9 covers ‘telecommunication machines and apparatus; personal digital assistants; smartphones; electronic machines, and apparatus and their parts.’
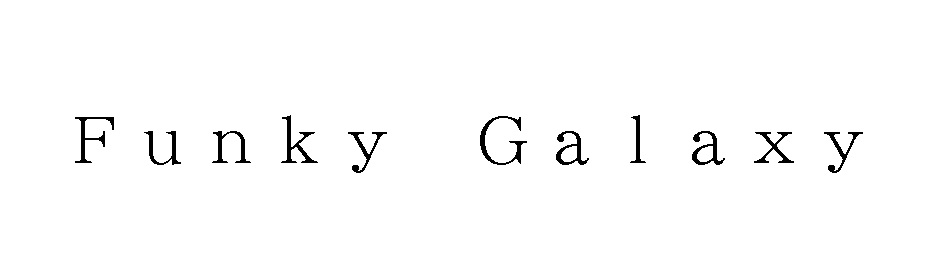
JPO granted protection of the “Funky Galaxy” mark and published for opposition on July 14, 2020.
Opposition by Samsung
On September 11, 2020, Samsung, the world’s largest smartphone maker famous for Galaxy series mobiles, filed an opposition and claimed the Opposed mark shall be canceled in relation to goods and services in class 9, 35, and 41 in contravention of Article 4(1)(vii), (x), (xi), (xv) and (xix) of the Trademark Law by citing its own senior TM Reg nos. 4498554 “Galaxy”, IR1335923 “GALAXY STUDIO”, and 6309820 “Galaxy Harajuku”.
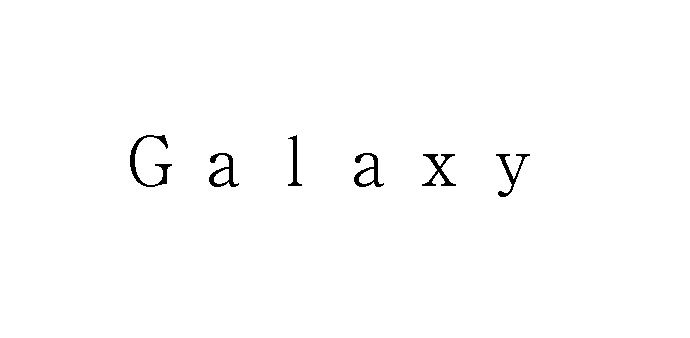
Article 4(1)(xv) is a provision to prohibit any mark from registering if it is likely to cause confusion with other business entities’ well-known goods or services.
Samsung argued the Opposed mark shall cause confusion with Samsung “Galaxy” especially when used on smartphones and related goods and services, given a remarkable reputation of “Galaxy” holding 3rd market share (7.4% in 2018, 8.0% in 2019, 9,0% in 2020) in Japan and the close resemblance between “Galaxy” and “Funky Galaxy”.
JPO Decision
The Opposition Board did not question a remarkable degree of reputation and popularity of trademark “Galaxy” as a source indicator of the opponent smartphones.
In the meantime, the Board did not consider the term “Galaxy” as a prominent portion of the opposed mark from visual and conceptual points of view. If so, the opposed mark shall be assessed in its entirety.
In the assessment of similarity of the mark, the Board found “Funky Galaxy” is visually and phonetically distinguishable from “Galaxy” due to the presence of “Funky.” From concept, both marks are less similar because the opposed mark does not give rise to a specific meaning and the opponent mark “Galaxy” means an extremely large group of stars and planets. Both marks have a low degree of similarity accordingly.
Even though “Galaxy” has been well-known as a source indicator of Samsung smartphones, and the goods and services in question are closely associated with smartphones, given a low degree of similarity between “Funky Galaxy” and “Galaxy”, the Board has a reasonable ground to believe that relevant consumers would not confuse a source of goods and services bearing the opposed mark “Funky Galaxy” with Samsung and any business entity economically or systematically connected with the opponent.
Based on the foregoing, the Board decided the allegations are groundless and the Opposed mark shall remain valid as the status quo.