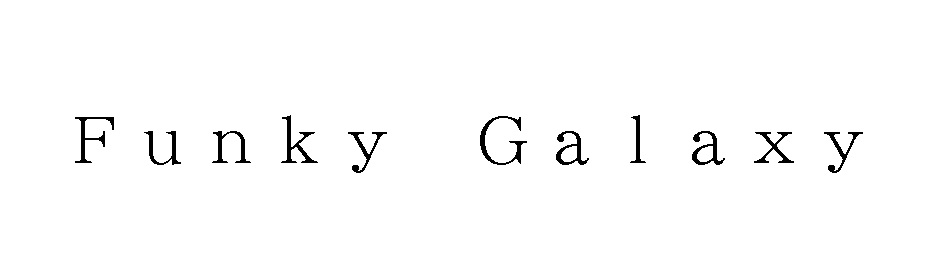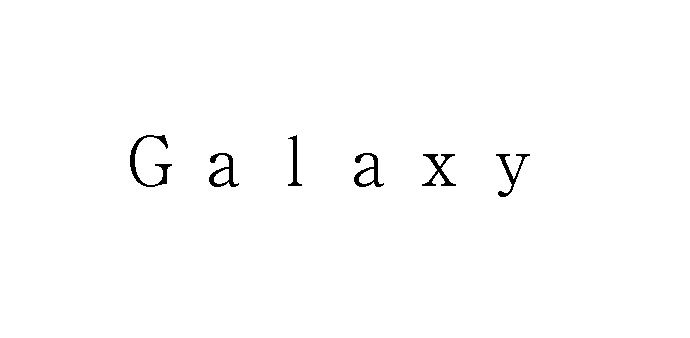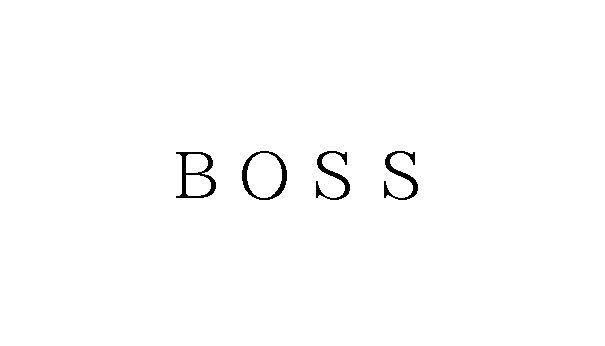Opposition
A trademark opposition is a proceeding in which a third party can oppose a newly registered trademark under Article 43bis of the Japan Trademark Law. For example, once a trademark is newly registered by JPO, this fact is published in the Official Gazette of Trade Marks immediately after it is actually registered. This kicks off a two (2) month period known as the ‘opposition period’ during which other parties are then given an opportunity to ‘oppose’ the registration of the trademark.
Invalidation
Trademark invalidation is an inter-partes proceeding in which a party has a legal interest in the result that can null a trademark registration under Article 46 of the Japan Trademark Law. If the registration is less than five years old, the party challenging the trademark rights can rely on any ground that could have prevented registration initially.
Comparison
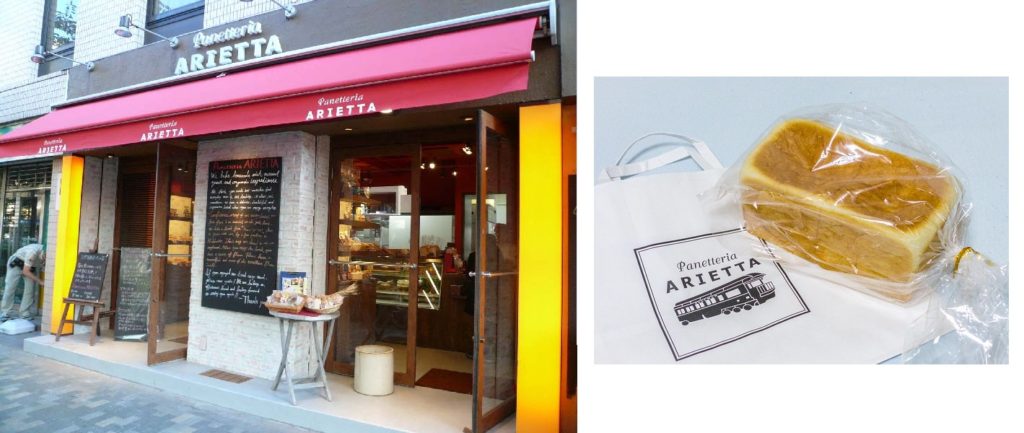
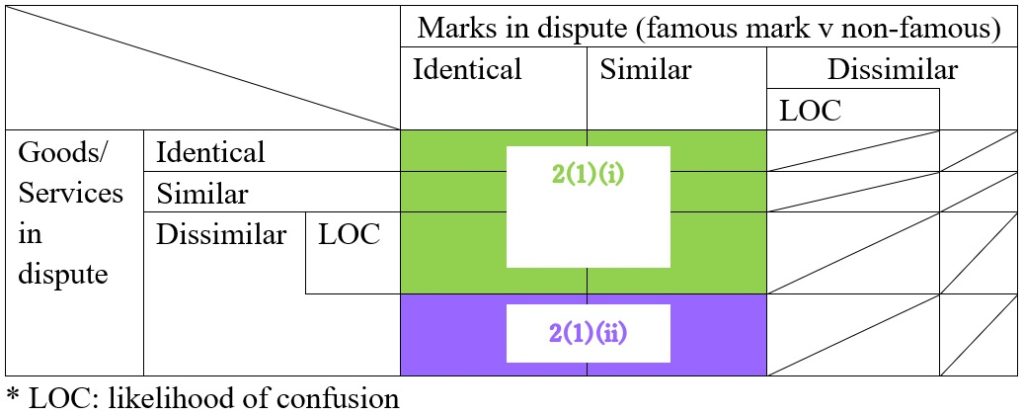
Conflict with earlier registration (similarity of mark and goods/service), a likelihood of confusion with famous mark, and descriptiveness are the most common grounds asserted both in opposition and invalidation action.
| Trademark Opposition | Trademark Invalidation | |
| Statute of limitations | 2 months from the publication date | 5 years from the registration date |
| Official fee | JPY11,000 for 1 class JPY19,000 for 2 classes | JPY55,000 for 1 class JPY95,000 for 2 classes |
| Standing | Legal interest is not required | Legal interest is required |
| Counterargument | No obligation to counterargue unless the JPO notifies a cancellation ground to a registrant. | Mandatory for a registrant to counterargue, otherwise it may adversely affect. |
| Pendency period | 7.9 months | 11.5 months |
| Appeal to decision | Only the registrant can file an appeal against an unfavorable decision | Either party can file an appeal against the JPO decision |
Which action to take?
From a cost-saving point of view, opposition undoubtedly looks more attractive than invalidation, however, when you look at the success rate of opposition (see below table), it may change your mind. There has been a big gap in the success rate between opposition and invalidation for years.
| Year | The success rate of the Opposition | The success rate of Invalidation |
| 2015 | 13% | 32% |
| 2016 | 16% | 42% |
| 2017 | 11% | 33% |
| 2018 | 11% | 34% |
| 2019 | 11% | 56% |
| 2020 | 11% | 35% |
Therefore, in terms of probability theory, invalidation action is by far preferable to opposition for the purpose of removing trademark registration in Japan.