On January 13, 2022, the Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an invalidation action filed by Apple Inc. against TM Reg no. 5770529 for device mark by finding an unlikelihood of confusion with the famous Apple design mark.
[Invalidation case no. 2020-890049]Disputed mark
Shelly Co., Ltd applied device mark (see below) for registration to be used on protection covers and cases for smartphones, protection covers and cases for tablets, cases for laptops in class 9 with the JPO on January 20, 2015.
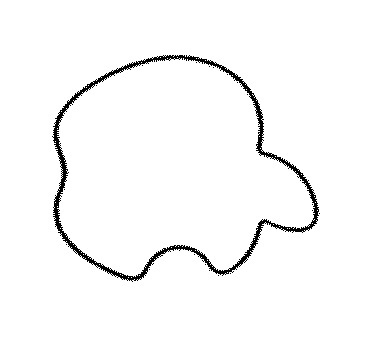
The mark was registered on June 12, 2015, without receiving a refusal during the substantive examination.
Invalidation action
Japan Trademark Law has a provision to retroactively invalidate trademark registration for certain restricted reasons specified under Article 46 (1) provided that the interested party files an invalidation petition within a five-year statute of limitations.
Apple Inc. filed a petition for invalidation against the disputed mark on June 12, 2020. Apple argued the mark shall be invalidated in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) of the Trademark Law due to a likelihood of confusion with its famous “bitten apple” logo (see below) when used on all goods in class 9.

Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entities’ well-known goods or services, to the benefit of brand owners and users.
JPO decision
The JPO did not question a remarkable degree of reputation and popularity of the Apple logo as a source indicator of Apple Inc. in connection with personal computers, smartphones, and any goods and services related to them.
In the meantime, the JPO found the disputed mark is dissimilar to the Apple logo. Because of a low degree of similarity, relevant consumers are unlikely to cause confusion with Apple Inc. when the disputed mark is used on the goods in question by stating that:
- From appearance, both marks are obviously dissimilar. Provided that it is adequate to rotate the disputed mark 90 degrees to the left and compare it with the Apple logo, the Board still has a reasonable ground to believe both marks are visually dissimilar because of distinctive features in detail and overall appearance.
- Both the disputed mark and the Apple logo would not give rise to any specific sound. If so, the marks are not comparable in pronunciation.
- The Apple logo gives rise to a meaning of “famous source indicator of Apple Inc.”. The disputed mark has no meaning. Therefore, both marks are dissimilar in concept.
Based on the foregoing, regardless of the famousness of the Apple logo and close association between the goods in question with Apple’s business and relevant consumers, the Board decided to dismiss the invalidation action.