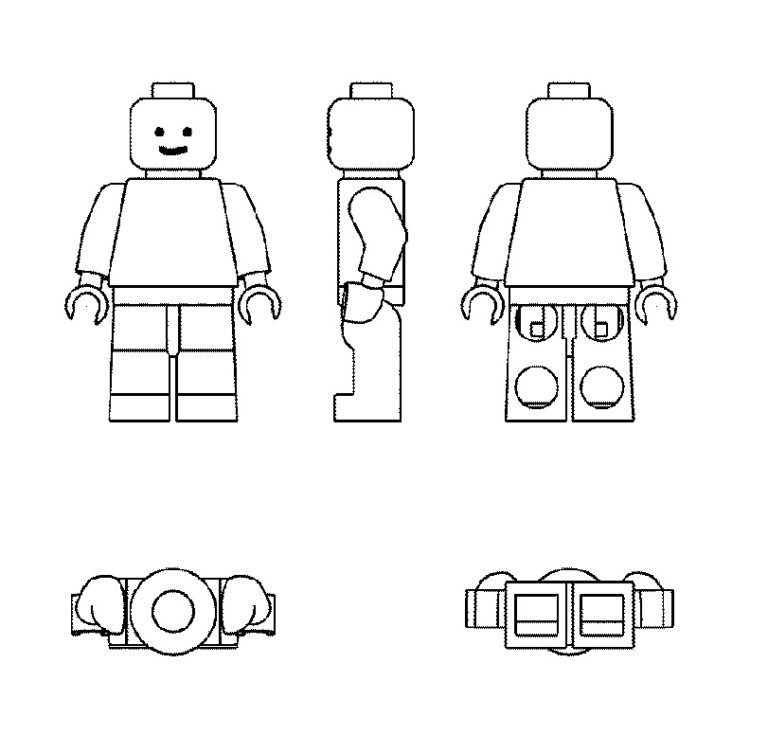
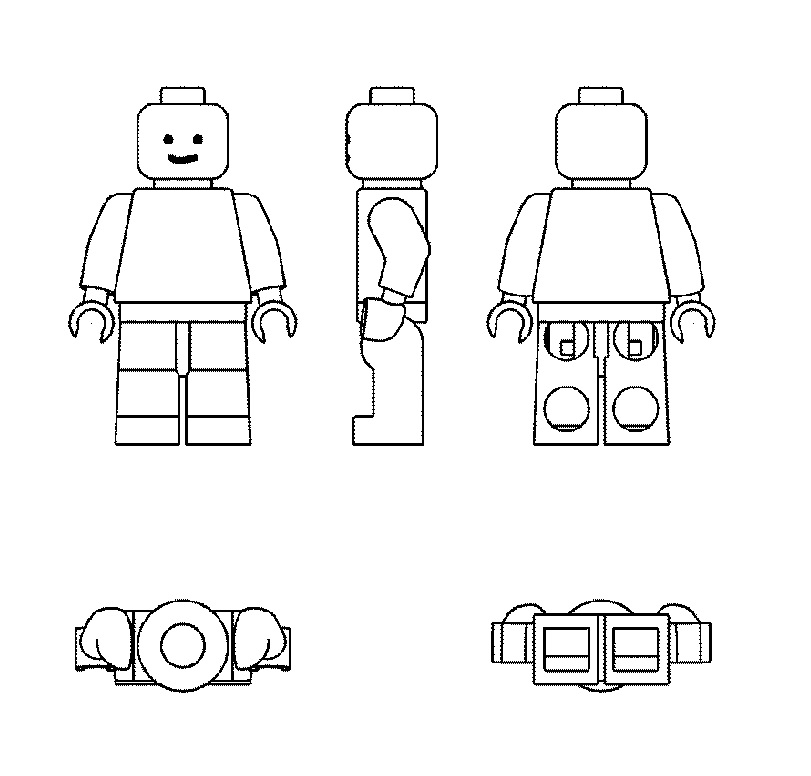
The JPO Appeal Board affirmed the examiner’s rejection and decided to refuse IR no. 1379178 for the 3D shape of the Volkswagen Beetle due to a lack of inherent and acquired distinctiveness in relation to goods of classes 9, 28, and 30.
[Appeal case no. 2020-650030, Gazette issued date: January 27, 2023]VW Beetle
German car giant Volkswagen AG filed a 3D mark representing the iconic VW Beetle car (see below) in relation to various goods including navigation apparatus for vehicles [onboard computers], toy automobiles, scale model automobiles of classes 9, 28, and 30 with the JPO via the Madrid Protocol on December 7, 2017.
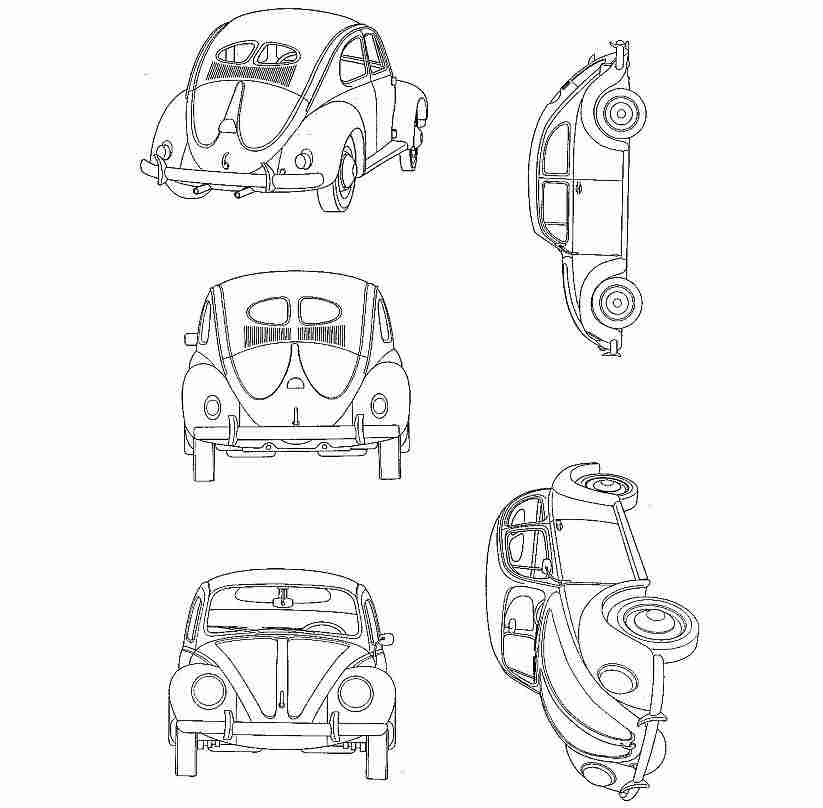
The JPO examiner rejected the mark in contravention of Article 3(1)(iii) and 4(1)(xvi) of the Japan Trademark Law on March 19, 2020, by stating that the mark merely represents a common shape of goods when used on toy automobiles, scale model automobiles of class 28 and chocolate and desserts, ice creams, frozen yogurts and sorbets of class 30, and consumers will misunderstand the quality of goods when used on other designated goods.
Appeal by Volkswagen
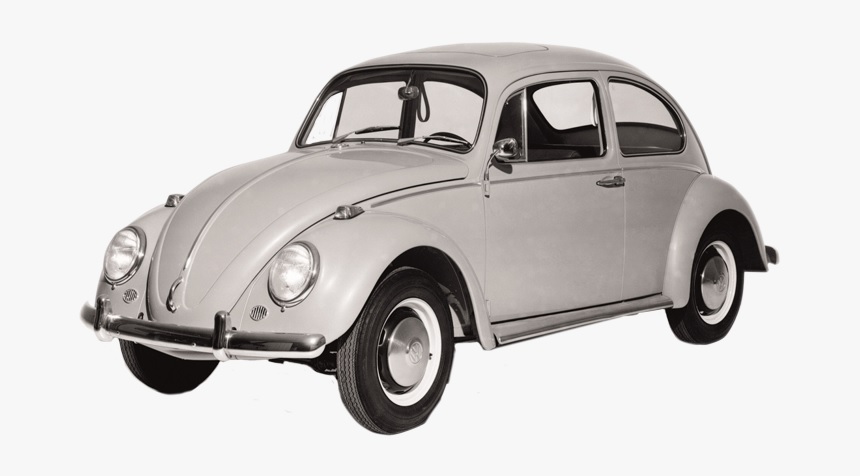
Volkswagen filed an appeal against the rejection on July 2, 2020, and argued the inherent and acquired distinctiveness of the 3D mark as a result of substantial use on VW’s automobiles (cl. 12) for more than six decades and around 21.5 million units cumulatively.

JPO Decision
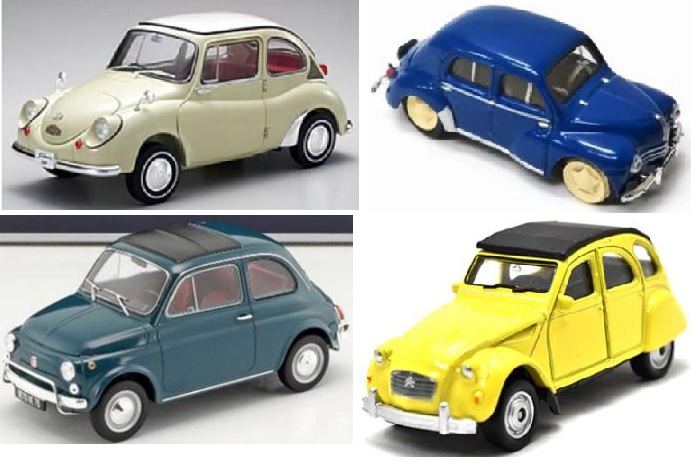
The Appeal Board at its discretion found plenty of goods in the shape of cars promoted for sale in relation to toy automobiles, scale model automobiles (cl. 28), and chocolate and desserts, frozen yogurts, and sorbets (cl. 30).
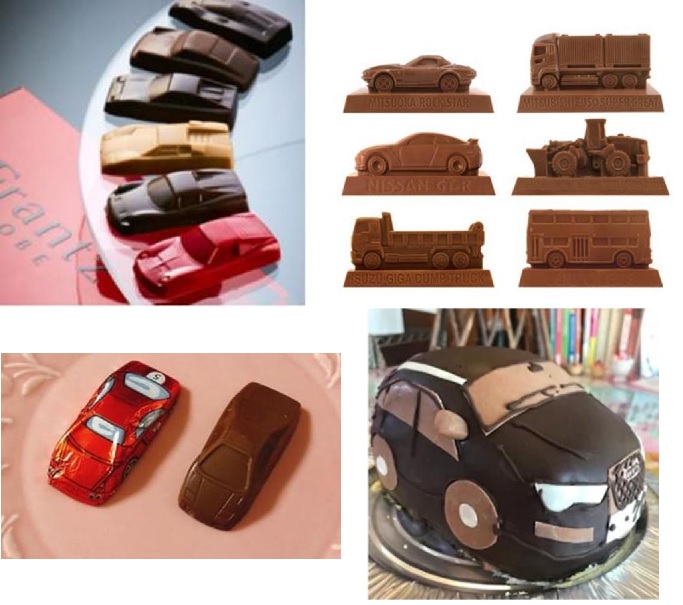


Bearing this fact in mind, the Board has a reason to believe the applied mark is adopted for a purpose of enhancing function or the aesthetic appeal of the goods in question. If so, the shape still remains within the scope of the descriptive shape of goods and shall be unregistrable due to a lack of inherent distinctiveness in relation to these goods.
Furthermore, the Board pointed out that Volkswagen stopped manufacturing cars in the shape of the applied mark in 2003. There is reasonable doubt that the 3D mark has been famous as a source indicator of VW cars after a lapse of twenty years. Besides, the applicant has not produced any evidence to demonstrate the actual use of the 3D shape on goods in classes 9, 28, and 30 and its sales.
Based on the foregoing, the Board found the 3D mark lacks inherent and acquired distinctiveness in relation to the goods in question and dismissed the appeal entirely.