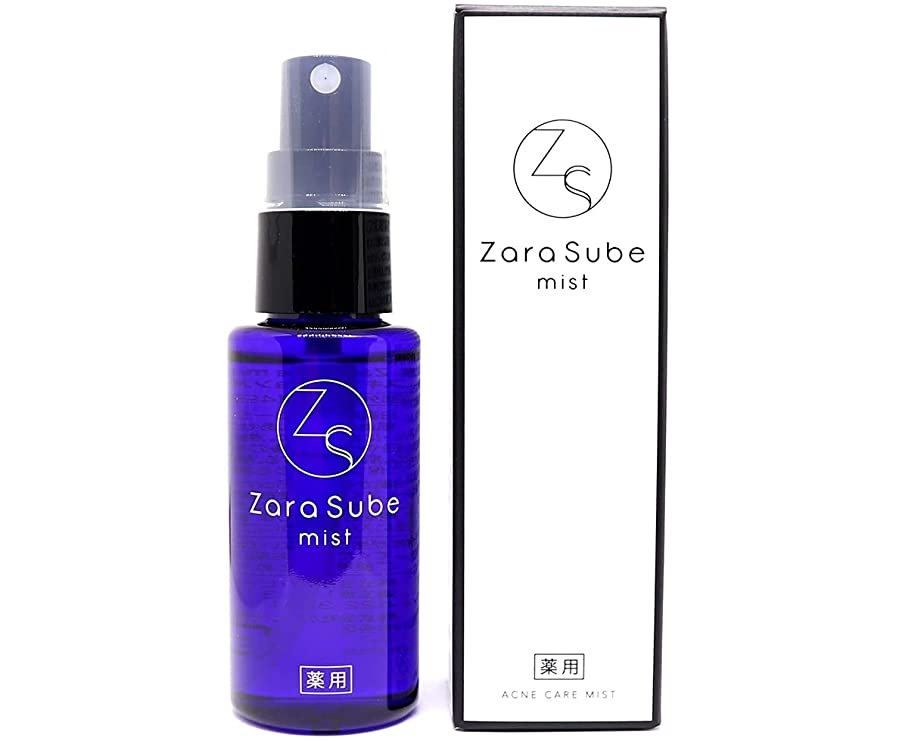
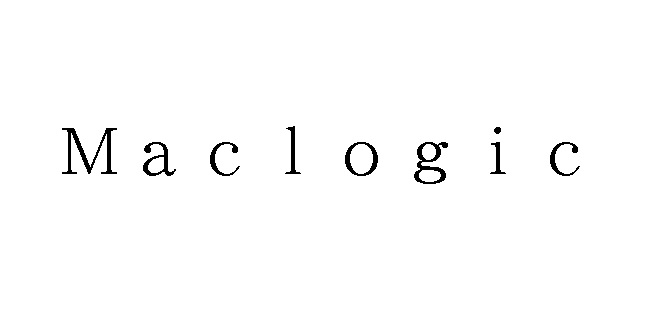On July 12, 2022, the Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition claimed by Italian fashion house Gucci against Japan Trademark Registration no. 6384970 for the mark “CUGGL” with a hand-painted line in pink by finding less likelihood of confusion with famous fashion brand “GUCCI”.
[Opposition case no. 2021-900284]CUGGL
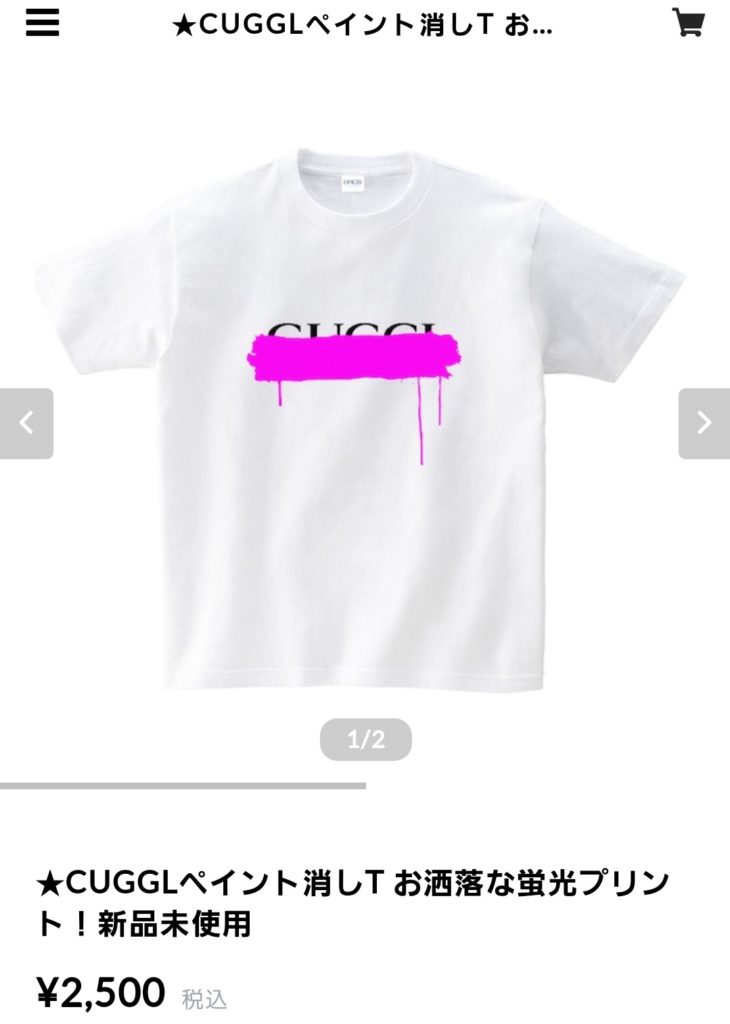
Opposed mark, consisting of the term “CUGGL” with a hand-painted line in pink, was applied for use on clothing, footwear, headwear, and apparel in class 25 by an individual on October 6, 2020.

The JPO granted protection of the opposed mark and published it for opposition on May 25, 2021.
Opposition by GUCCI
Italian high-end luxury fashion house, GUCCI filed an opposition with the JPO on July 26, 2021, and argued the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(vii), (xv), and (xix) of the Trademark Law due to similarity and likelihood of confusion with famous fashion brand “GUCCI”.
GUCCI claimed the opposed mark was sought with malicious intention to free-ride goodwill and reputation in a manner of hiding the lower part of the term “CUGGL” by a pink painted line to the extent consumers could recognize it as if “GUCCI”. In fact, the registrant promotes T-shirts bearing the opposed mark with the most part of the term hidden.
JPO Decision
The JPO Opposition Board admitted a remarkable degree of popularity and reputation of the opponent’s “GUCCI” mark.
In the meantime, the Board did not find a resemblance between “GUCCI” and “CUGGL” from visual, phonetic, and conceptual points of view. Due to a low degree of similarity of the mark, the Board had no reason to believe that relevant consumers would misconceive a source of goods in question bearing the opposed mark from GUCCI or any entity systematically or economically connected to the opponent.
Assuming a low degree of similarity of the mark and less likelihood of confusion, the Board can’t find a reasonable ground to admit the applicant had a malicious intention to free-ride goodwill and reputation of GUCCI and do harm to the opponent.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO dismissed the entire allegations and decided the opposed mark was valid.