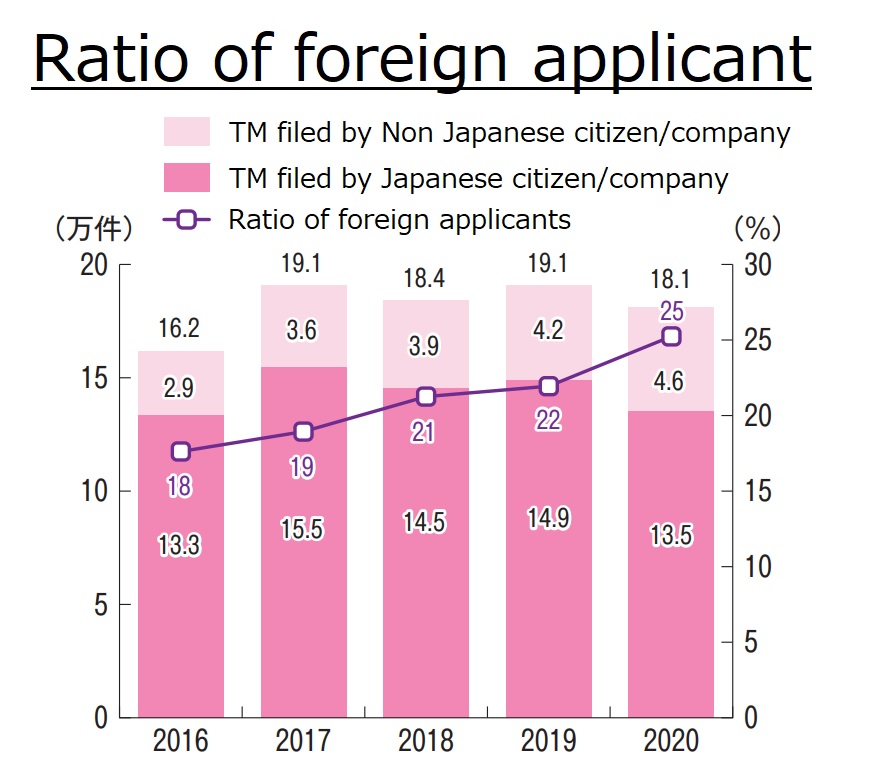
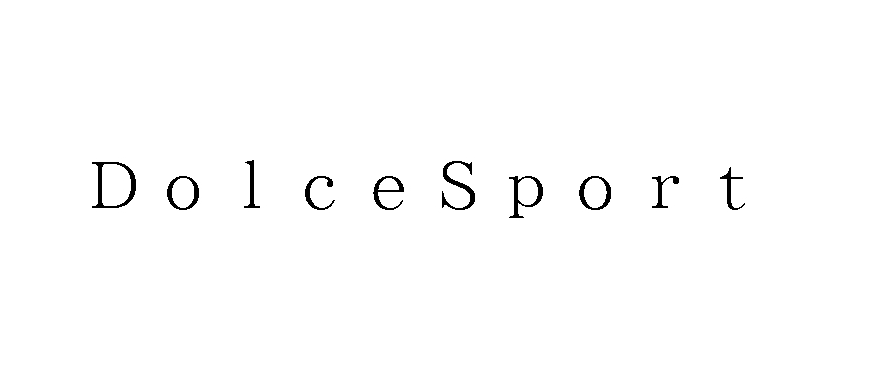The Japan Patent Office sided with Sony Corporation and declared invalidation of TM Registration no. 5764615 for wordmark “SONICODE” due to a likelihood of confusion with “SONY”.
[Invalidation case no. 2020-890039, Gazette issued date: July 30, 2021]SONICODE
Field System Inc., a mobile application developer, applied wordmark “SONICODE” in standard character for registration on various goods including telecommunication apparatus, electronic machines, consumer video game programs, and its related services in class 9, 38, and 41 with the JPO on December 12, 2014 (TM App no. 2014-105218).
The mark did not face any refusal during the substantive examination and it was registered on date May 15, 2015.
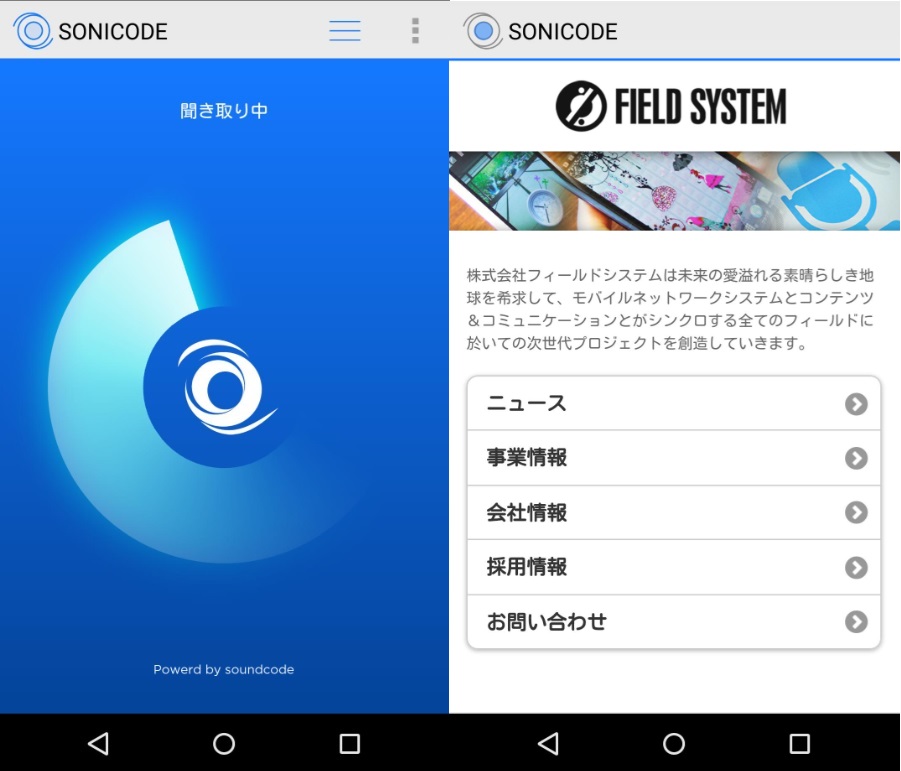
Apparently, the mark has been used on mobile applications for smartphones.
SONY
SONY CORPORATION, a major Japanese manufacturer of consumer electronics products, filed an opposition against the SONICODE mark on August 5, 2015, before the lapse of a two-month statutory period for the opposition, in contravention of Article 4(1)(xi), (xv), and (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law. However, the JPO Opposition Board found both marks dissimilar and no likelihood of confusion between the marks SONY and SONICODE and dismissed SONY’s allegations entirely. [Opposition case no. 2015-900260]
On May 12, 2020, just three days before the lapse of the five-year statute of limitations, SONY CORPORATION files a petition for invalidation and alleged that the contested mark shall be invalidated based on Article 4(1)(x), (xi), (xv).
SONY argued that relevant consumers would conceive SONY at the sight of the contested mark SONICODE because of a high reputation of SONY and less distinctiveness of the term “CODE” in relation to the goods and services in question.

To bolster the arguments, SONY demonstrated how AI speakers, e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Assist, Microsoft Cortana, Apple Siri, reacted to hear “SONICODE”. Allegedly, the AI speakers recognized it as ‘SONY code’ or ‘SONY cord’ and displayed information relating to SONY.
Field System Inc. did neither answer to the petition nor dispute at all during the invalidation procedure.
JPO decision
The JPO Invalidation Board did not question a remarkable degree of reputation, popularity, and originality of “SONY” as a source indicator of the opponent’s business and its products (telecommunication apparatus, electronic machines, consumer video game programs).
Besides, the Board found the prefix “SONI” of the contested mark gives rise to a similar appearance and pronunciation with “SONY”. Relevant consumers are likely to consider that the contested mark consists of “SONI” and “CODE”. If so, even if both marks are deemed dissimilar in their entirety, the Board has good reason to believe “SONICODE” has a certain degree of similarity to “SONY”.
In view of a close association between the goods and services in question and the opponent business, the Board concluded the contested mark shall be retroactively invalidated in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv). In the meantime, because of the dissimilarity of the marks, the Board dismissed allegations based on Article 4(1)(x) and (xi).