The Opposition Board of the Japan Patent Office (JPO) decided in favor of Bentley Motors Limited, the definitive British car company, in their attempt to oppose the registration of the trademark consisting of a copied winged B logo and “BENTLEY LIFE” in connection with educational services and others of class 41.
[Opposition case no. 2018-900160, Gazette issued on September 25, 2020]
Opposed mark
Opposed mark (TM Registration no. 6031879), consisting of a copied winged B logo and a word “BENTLEY LIFE” (see below), was applied for registration on August 3, 2017, for ‘health club services [health and fitness training]; club services [entertainment or education]; teaching and educational services; organization of competitions [education or entertainment]; presentation of movies; arranging and conducting of workshops [training]’ in class 41 by UK Arthur Brand Management Company Limited.

The mark was published for registration on April 24, 2018, without confronting any office action from the JPO examiner.
Opposition by Bentley Motors Limited
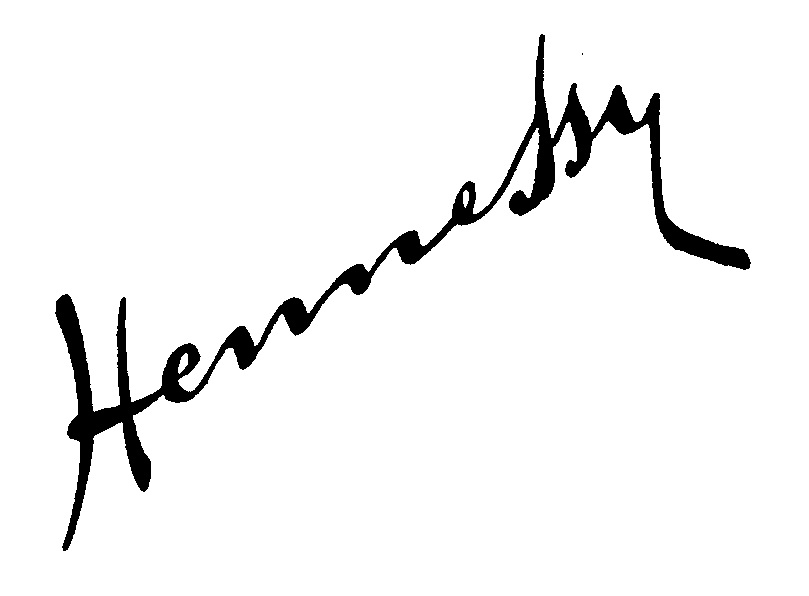
On June 22, 2018, before the lapse of a two-months opposition period, Bentley Motors Company Limited filed an opposition before the JPO and claimed that the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(vii), (xv) and (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law by citing trademark registration for its iconic Winged B logo and the BENTLEY wordmark (see below) in class 12, which the opponent allegedly has used on luxury cars since the 1920s.


Article 4(1)(vii) prohibits any mark likely to cause damage to public order or morality from registration.
Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entity’s well-known goods or services, to the benefit of brand owner and users’ benefits.
Article 4(1)(xix) prohibits registering a trademark that is identical with, or similar to, other entity’s famous mark, if such trademark is aimed for unfair purposes, e.g. gaining unfair profits, or causing damage to the entity.
Bentley argued that both the winged B logo and its tradename has unquestionably acquired a high degree of reputation and popularity as a source indicator of the opponent cars. It is evident that the figurative element of the opposed mark is almost identical with a renowned winged B logo and the literal element of the opposed mark contains “BENTLEY”. If so, the opposed mark resembles the cited marks closely.
Bentley also strongly alleged that the applicant must have acquainted with the cited mark and filed the opposed mark with a fraudulent intention to deceive or free-ride.
JPO Decision
The JPO Opposition Board admitted Bentley’s winged B logo, as well as its tradename, has become famous among relevant traders in the car business and consumers interested in automobiles as a result of continuous use since the 1920s.
Given the close resemblance between the opposed mark and the cited marks, even if the services in question are remotely associated with cars, there still exists a possibility that consumers may confuse the source of services bearing the opposed mark with Bentley by taking into consideration a high degree of reputation and originality of the winged B logo and “BENTLEY”.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO sided with Bentley and decided to cancel the opposed mark in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv).