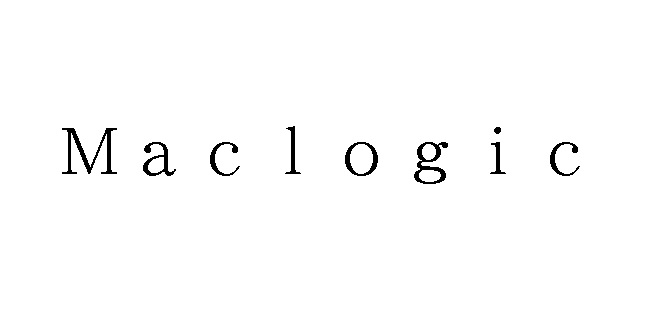The Japan Patent Office (JPO) did not side with McDonald in opposition against Japanese TM Reg no. 6575774 for stylized wordmark “mac” in class 35 due to dissimilarity to “Mc” and unlikelihood of confusion with McDonald.
[Opposition case no. 2022-900294, decided on August 15, 2023]Opposed mark “mac”
The opposed mark, consisting of a stylized word “mac” (see below), was filed by Daiya Group Inc. for use on retail services or wholesale services for various goods including, meat, milk, carbonated drinks [refreshing beverages] and non-alcoholic fruit juice beverages, tea, coffee and cocoa in class 35 with the JPO on October 27, 2021.

The applicant has used the opposed mark as a tradename of their drug store “mac”.
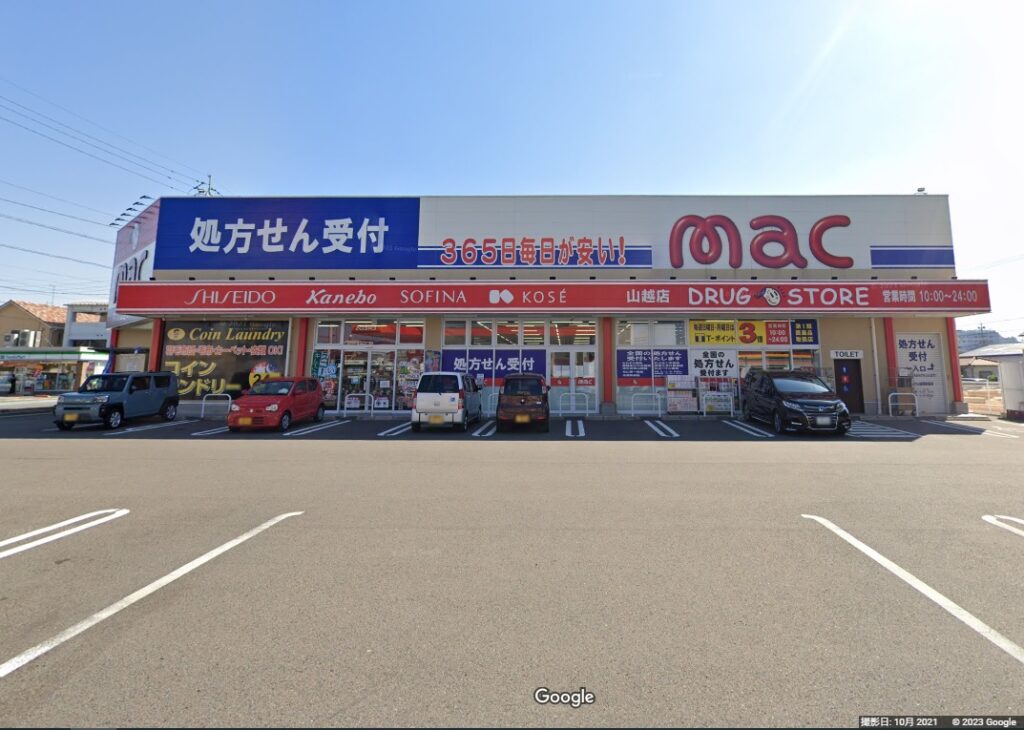

The JPO granted protection of the opposed mark on June 22, 2022 and published it for post-grant opposition on June 30, 2022.
Opposition by McDonald
McDonald International Property Company Limited filed an opposition against the opposed mark on July 20, 2022 with the JPO and claimed cancellation of the opposed mark in contravention of Article 4(1)(x), (xi) and (xv) of the Japan Trademark Law based on earlier trademark registrations and various marks used in relation to their business.

McDonald argued that the mark “Mc” has been remarkably famous as a source indicator of the opponent and it gives rise to a same sound with the opposed mark “mac”. If so, relevant consumers would confuse the source of retail services or wholesale services for meat, milk, carbonated drinks [refreshing beverages] and non-alcoholic fruit juice beverages, tea, coffee and cocoa bearing the opposed mark with McDonald due to close resemblance of the marks and relatedness to food business.
JPO decision
The Opposition Board pointed out McDonald has been regularly using the mark “Mc” in a tight combination with other word. Regardless of the fact that consumers are accustomed to call McDonald as “MAC”, there is no evidence to show the opponent has used “MAC” in connection with their business.
By taking account of insufficient evidence to demonstrate substantial recognition of the cited marks, the Board has no reason to admit famousness of the mark “Mc” as a source indicator of McDonald.
In assessing the similarity of mark, the Board found the cited marks are aurally dissimilar to the opposed mark since they are pronounced as “emˈsiː” or “mækˈkæfˈeɪ” in its entirety. Besides, there is no ground to find visual and conceptual similarity of respective mark. If so, the Board believes the opposed mark is clearly dissimilar to the cited marks.
To the extent that there is insufficient evidence to support how the term “MAC” has played a significant role in indicating the source of McDonald, the Board held it unlikely that relevant consumers confuse the opposed mark with McDonald when used on the services in question.
Based on the foregoing, the Board dismissed the opposition entirely and decided that the opposed mark “mac” shall remain valid as the status quo.