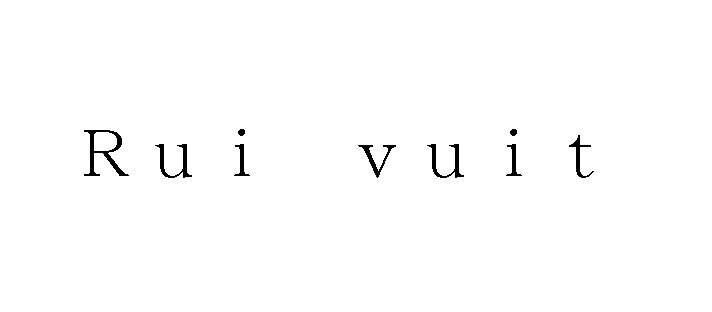The Japan Patent Office (JPO) decided to cancel TM Reg no. 6576001 for word mark “BORDEAUX WAVE” in relation to cosmetics due to contrary to public policy and accepted principles of morality.
[Opposition case no. 2022-900374, decided on September 1, 2023]Opposed mark “BORDEAUX WAVE”
KAO Corporation, a major Japanese company providing a broad range of household products such as cosmetics and detergents, filed a trademark application for the wordmark “BORDEAUX WAVE” with its transliteration written in Japanese Katakana character (see below) for use on soaps and detergents, cosmetics, perfume and flavor materials, incense in class 3 with the JPO on December 22, 2021.

Apparently, the mark is used as a name for one of the RMK lipstick colors distributed by KAO’s subsidiary company.
The JPO examiner did not raise any objection to the “BORDEAUX WAVE” mark and granted protection on June 2, 2022.
Trademark Opposition
On August 31, 2022, before the lapse of a two-month statutory period counting from the publication date, INSTITUT NATIONAL DE L’ORIGINE ET DE LAQUALITE and CONSEIL INTERPROFESSIONNEL DUVIN DE BORDEAUX as joint opponents filed an opposition against the BORDEAUX WAVE mark and claimed the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(vii) of the Japan Trademark Law.
The opponents argued that the opposed mark misleads as to the origin of the goods in question on which it is used since the GI “Bordeaux” has been widely known for an origin of French Wine. Besides, the opposed mark severely harms to fame and aura of prestigious wine constituted under the strict control of domicile of origin.
Article 4(1)(vii)
Article 4(1)(vii) prohibits any mark likely to offend public order and morals from registering.
Trademark Examination Guidelines sets forth criteria for the article and samples.
- Trademarks that are “likely to cause damage to public order or morality” are, for example, the trademarks that fall under the cases prescribed in (1) to (5) below.
(1) Trademarks which are, in composition per se, characters or figures, signs, three-dimensional shapes or colors or any combination thereof, or sounds that are unethical, obscene, discriminative, outrageous, or unpleasant to people. It is judged whether characters, figures, signs, three-dimensional shapes or colors or any combination thereof, or sounds are unethical, discriminative or unpleasant to people, with consideration given to their historical backgrounds, social impacts, etc. from a comprehensive viewpoint.
(2) Trademarks which do not have the composition per se as prescribed in (1) above but are liable to conflict with the public interests of the society or contravene the generally-accepted sense of morality if used for the designated goods or designated services.
(3) Trademarks with their use prohibited by other laws.
(4) Trademarks liable to dishonor a specific country or its people or trademarks generally considered contrary to the international faith.
(5) Trademarks whose registration is contrary to the order predetermined under the Trademark Act and is utterly unacceptable for lack of social reasonableness in the background to the filing of an application for trademark registration.
- Examples that fall under this item
(i) Trademarks that contain characters such as “university” and are likely to be mistaken for the name of universities, etc. under the School Education Act.
(ii) Trademarks that contain characters such as “士(shi)” which are likely to mislead that they represent national qualifications.
(iii) Trademarks of the name of a well-known or famous historical personage which are determined to have the risk of taking a free ride on public measures related to that personage and damage the public interests by inhibiting the performance of such measures.
(iv) Trademarks with figures indicated in a manner that may impair the dignity and honor of national flags (including foreign national flags)
(v) A sound mark related to the services of “medical treatment” which causes people to recognize siren sounds generated by ambulances that are well known in Japan.
(vi) A sound mark which causes people to recognize national anthems of Japan and other countries.
JPO Decision
The JPO Opposition Board found in favor of opponents that “BORDEAUX” has acquired a high degree of popularity and reputation among Japanese consumers as a source indicator of wines originated from the Bordeaux district.
Since the opposed mark contains the term “BORDEAUX”, it is undeniable that consumers are likely to connect the opposed mark with BORDEAUX wine or its district even when used on cosmetics and other goods in question. If so, the Board has a reason to believe that the opposed mark free-rides or dilutes lure and image of BORDEAUX wine, and adversely affects domicile of origin strictly controlled by French government. Thus, inevitably the opposed mark may cause disorder to a world of global commerce in a manner inconsistent with international fidelity.
Based on the foregoing, the Board decided to cancel the BORDEAUX WAVE mark entirely based on Article 4(1)(vii).