The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition filed by Jaguar Land Rover Ltd. against trademark registration no. 6244325 for word mark “Like a Jaguar” on cosmetics and other goods in class 3 by finding dissimilarity and unlikelihood of confusion with “JAGUAR.”
[Opposition case no. 2020-900165, Gazette issued date: December 14, 2020]
Opposed mark
An opposed mark consists of the term “Like a Jaguar” in a gothic type and its transliteration in a Japanese katakana character as below.

The mark was filed by KOSE Corporation on May 10, 2019, for use on ‘cosmetics; soaps and detergents; dentifrices; perfume and flavor materials; incense; breath-freshening preparations; false nails; false eyelashes; cosmetic cotton wool; fabric softeners for laundry use; adhesives for affixing false eyelashes; adhesive paper; cotton sticks for cosmetic purposes’ in class 3.
JPO, going through substantive examination, admitted registration and published for post-grant opposition on April 28, 2020.
Apparently, KOSE uses the mark “Like a Jaguar” to represent a lipstick color for ‘ADDICTION The Lipstick Satin’ 008.
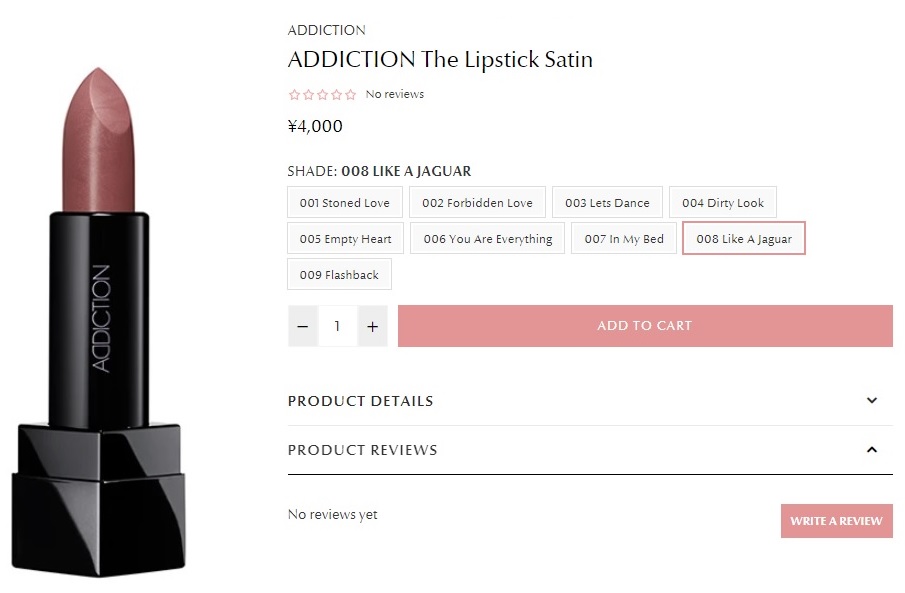
Opposition by Jaguar Land Rover
Jaguar Land Rover Ltd. filed a trademark opposition on June 25, 2020, before the JPO and claimed that the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(viii), (xi), and (xv) of the Trademark Law by citing trademark registrations for its iconic logo consisting of the image of a leaping jaguar and the word “JAGUAR” (see below), which allegedly has been used on the opponent’s products since 1935.

Article 4(1)(viii) prohibits registration of trademarks that contain the representation or name of any person, famous pseudonym, professional name or pen name of another person, or famous abbreviation thereof for the purpose of protecting the personal rights of a living individual.
Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to prohibit registering a junior mark that is deemed identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entity’s well-known goods or services, to the benefit of a brand owner as well as users’ benefits.
Jaguar Land Rover argued that the opposed mark has been confusingly similar to the cited mark since the opposed mark “Like a Jaguar” gives rise to a meaning of ‘Similar to Jaguar’ in its entirety. Besides, given the mark “JAGUAR” has obtained a high level of popularity among relevant consumers as a source indicator of the opponent’s motorcars, apparels, fragrances, and other licensed goods, the consumers would notice the term “Jaguar” as a dominant portion of the opposed mark and thus confuse or misconceive it with the opponent consequently.
JPO decision
The Opposition Board did not admit a high level of popularity of the cited mark by stating that the opponent failed to produce sufficient evidence in an objective manner. According to the allegation, opponents sold more than 100,000 cars around the globe in 2019. But relevant evidence was not produced to demonstrate the sales. Due to this reason, it is unknown how many cars of the opponent were sold in Japan. Likewise, there was little evidence to show a high recognition of the cited mark in relation to goods other than cars.
Provided that the mark “JAGUAR” was found insufficiently famous for the opponent cars, the Board has no reason to believe that relevant consumers would see the term “Jaguar” of the opposed mark as a dominant source indicator. If so, both marks shall be assessed in their entirety.
The opposed mark gives rise to a meaning of ‘similar to a large spotted wild cat of South America’ and a pronunciation of ‘laɪk ə dʒæɡ.wɑːr’. The term “Like a” sufficiently differentiates the opposed mark from the cited mark in appearance, sound, and concept.
Based on the foregoing, the Board found relevant traders and consumers are unlikely to confuse or associate the opposed mark with the opponent or any business entity economically or systematically connected with Jaguar Land Rover when used on the goods in question. In conclusion, the opposed mark shall remain valid as the status quo.
























