The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition claimed by Visa International Service Association (VISA) against TM Reg no. 6512071 for the wordmark “AIRVISA” due to an unlikelihood of confusion with “VISA” in connection with goods and services of classes 9, 35, 39, and 42.
[Opposition case no. 2022-900159, decided on March 9, 2023]AIR VISA
SmartHR, Inc. filed the wordmark “AIRVISA” in standard character for use on various goods and services in classes 9, 35, 39, and 42, inter alia, computer application software, personal management, application service of working visa and residence status, and SaaS with the JPO on July 29, 2021.

AIRVISA Inc., a subsidiary of SmartHR, provides services for Japanese companies to support online working visa applications and residence status management for their foreign workers.
The JPO granted protection of the AIR VISA mark on February 1, 2022, and subsequently, the mark was published for opposition on February 21, 2022.
Opposition by VISA
Visa International Service Association (VISA) filed an opposition on April 21, 2022, before the lapse of a two-month opposition period, and contended that the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) of the Japan Trademark Law.
Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entities’ well-known goods or services.
VISA argued relevant consumers would conceive of VISA’s famous service mark “VISA” at the sight of the opposed mark, consisting of “AIR” and “VISA” when used on its designated goods and services because of a remarkable degree of the reputation of the “VISA” mark and business circumstances that credit card companies provide application program for online payment service at present

JPO decision
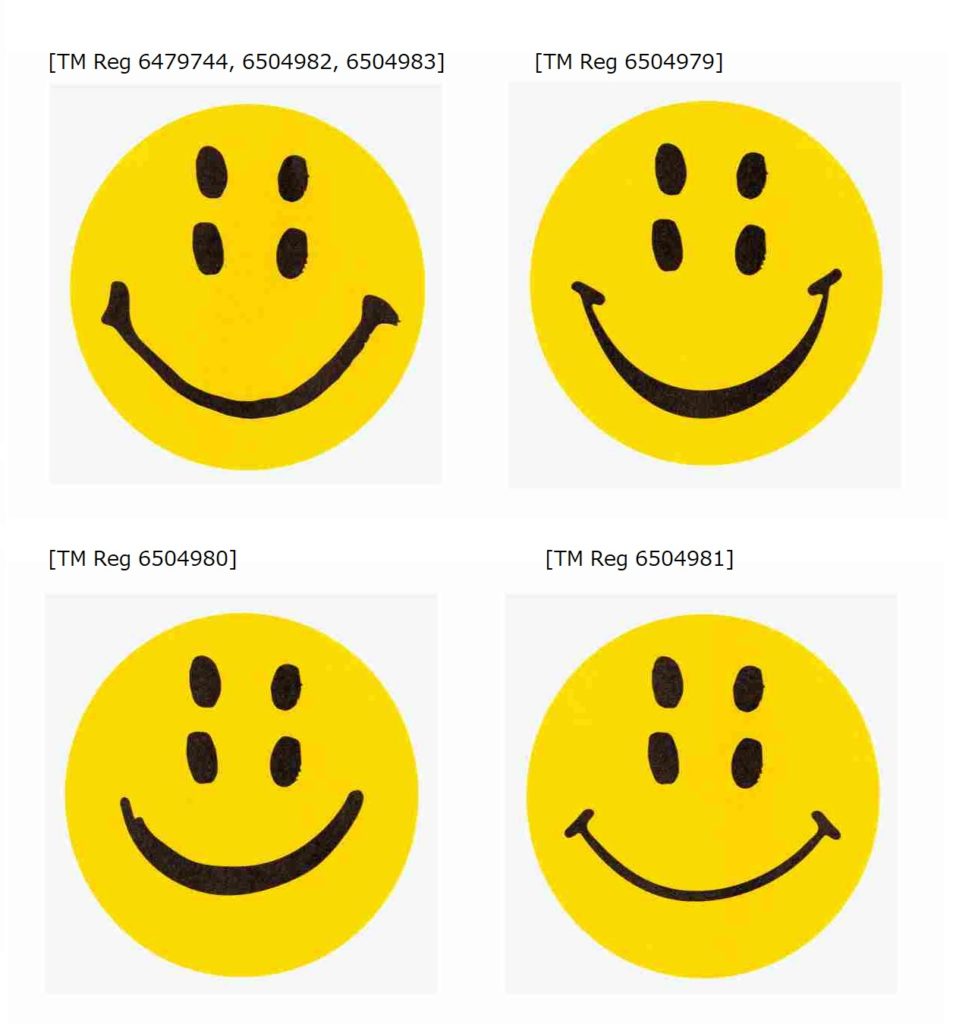
The JPO Opposition Board admitted the famousness of the “VISA” mark in relation to the service of credit card services and electronic credit card transaction processing as a source indicator of the opponent based on substantial use since 1958 and a top market share of over 50% in Japan.
In the meantime, the Board questioned whether the “VISA” mark has become famous as a source indicator in connection with computer programs for online payment services from the produced evidence.
The Board considered the opposed mark “AIR VISA” shall be assessed in its entirety because of a tight combination of two words that is familiar to relevant consumers in Japan respectively. If so, both marks are dissimilar in the presence and absence of the term “AIR” from visual, phonetical, and conceptual points of view.
Bearing in mind that the term “VISA” is not a coined word, having its original meaning as an official mark, usually made in a passport, that allows one to enter or leave a particular country, the Board has a reason to believe that relevant consumers are unlikely to associate the goods and services in question bearing the opposed mark with VISA.
Based on the foregoing, the Board decided the opposed mark shall not be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(xv) of the Trademark Law and dismissed the entire allegations by VISA.