The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition filed by HACHETTE FILIPACCHI PRESSE, Société Anonyme (FR) against Japanese trademark registration no. 6378600 for wordmark “RIELLE riche” by finding dissimilarity to and less likelihood of confusion with French fashion magazine “ELLE”.
[Opposition case no. 2021-900263, Gazette issued date: May 27, 2022]RIELLE
Opposed mark, consisting of the term “RIELLE” and the other term “riche” depicted below in small font (see below), was applied for registration on April 9, 2020, for various goods belonging to classes nos. 9, 14, 18, and 25 by SOLO PRODUCTS Co., Ltd., a Japanese company.

The JPO granted protection on April 13, 2021, and published for opposition on May 11, 2021.
Opposition by ELLE
On July 8, 2021, before the lapse of a two-month opposition period, HACHETTE FILIPACCHI PRESSE, Société Anonyme (hereinafter referred to as HFP), a French company responsible for the well-known women’s magazine ELLE, which had the largest readership of any fashion magazine in the world, with culturally specific editions published on six continents in the early 21st century, filed an opposition to “RIELLE”.
In the opposition, HFP contended that the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(xi) and (xv) of the Japan Trademark Law.
Article 4(1)(xi) is a provision to refrain from registering a junior mark that is identical with, or similar to, any senior registered mark.
Article 4(1)(xv) provides that a mark shall not be registered where it is likely to cause confusion with other business entities’ well-known goods or services, to the benefit of the brand owner and users.
HFP argued that the opposed mark is similar to HFP’s earlier registrations for the mark “ELLE” and relevant consumers are likely to confuse or misconceive the opposed mark with HFP or any business entity systematically or economically connected with the opponent due to the high popularity of opponent’s fashion brand “ELLE” and the close resemblance between the opposed mark and “ELLE”.
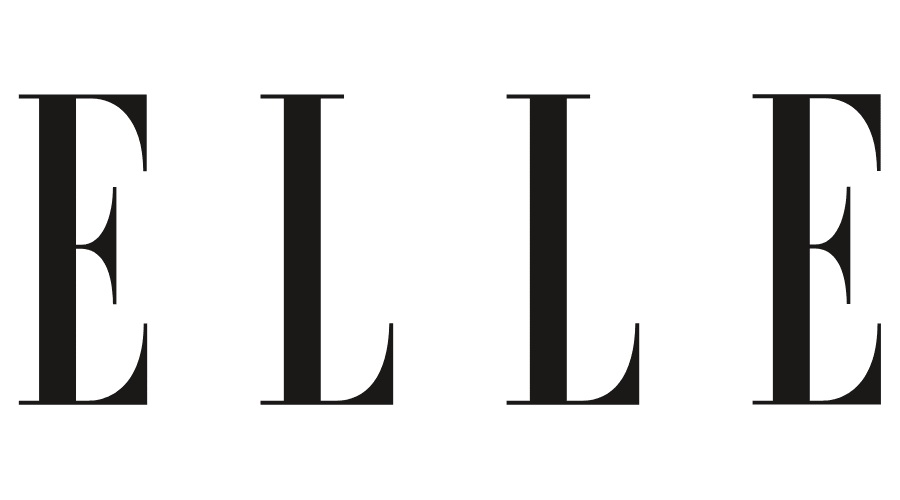
Board decision
The Board admitted the “ELLE” mark has acquired a high degree of reputation and popularity among relevant consumers and traders as a source indicator of the opponent in connection with magazines, online magazines as well as fashion and daily items.
In the meantime, the Board found that a prominent portion of the opposed mark “RIELLE” is dissimilar to the “ELLE” mark from visual, phonetical, and conceptual points of view.
Taking into consideration a quite low degree of similarity between the marks, the Board had no reason to believe that relevant consumers would mistakenly assume the opposed goods originate from the same source as or are associated with, the opponent when used on goods in question. Besides, being in mind that the term “ELLE” is a French word meaning “she” in English, the opponent mark shall not be strong.
The Board considered it is unlikely that relevant consumers would conceive of the “ELLE” mark from the term “RIELLE” because of an indivisible combination between “RI” and “ELLE” in the configuration of the opposed mark.
Based on the foregoing, the Board concluded that relevant traders or consumers would not confuse or misconceive a source of the opposed mark with HFP or any entity systematically or economically connected with the opponent when used on any goods in classes 9, 14, 18, and 25 and dismissed the opposition entirely.