The Japan Patent Office (JPO) dismissed an opposition claimed by Shangri-La Hotels against TM Reg no. 6610570 for the mark “Shangri-La-Golf” in class 35 due to dissimilarity between “Shangri-La” and “Shangri-La-Golf”.
[Opposition case no. 2022-900465, decided on July 26, 2023]Opposed mark
A Japanese individual filed a stylized word mark “Shangri-La-Golf” (see below) for use on retail and wholesale services in relation to woven fabrics, beddings, clothing, footwear, and personal articles in class 35 with the JPO on June 22, 2020.
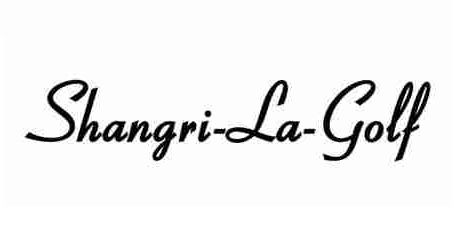
The JPO examiner rejected the mark in contravention of Article 4(1)(xi) of the Japan Trademark Law by citing earlier trademark registrations for wordmark “SHANGRI-LA”.
However, as a result of the JPO Appeal Board’s decision that found dissimilar to “SHANGRI-LA”, the mark could be registered on September 6, 2022.
Opposition by Shangri-La Hotels
Shangri-La International Hotel Management Ltd filed an opposition against the opposed mark on November 11, 2022 and argued the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(vii), (viii), (x), (xi), (xv), and (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law due to a remarkable degree of recognition of the cited mark “Shangri-La” and close resemblance between the opposed mark and “Shangri-La”.
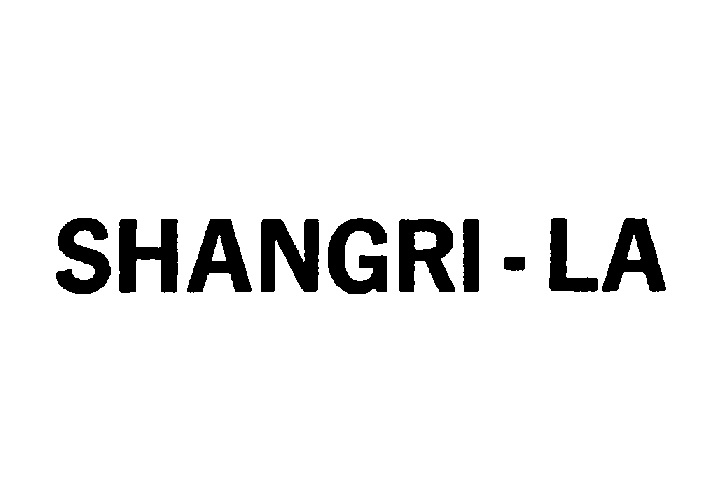
JPO decision
The JPO Opposition Board questioned a remarkable degree of recognition of the cited mark among relevant public in Japan by stating that the produced evidence is insufficient to find such recognition objectively.
As for appearance, sound and meaning of the opposed mark, the Board found
“The opposed mark consists of “Shangri”, “La”, and “Golf” written in the same font and size, and tightly united by a hyphen (-). Visually, there is no reason to find respective element perse independently plays a role in source indicator of the opposed mark. Besides, the sound arising from the opposed mark as a whole can be pronounced easily.
Even if the term “Golf” has the meaning of a kind of ball game, it is reasonable to find that the term would not be recognized as directly indicating a descriptive meaning or specific quality of the services in question. Relevant consumers would see the opposed mark as a whole.
Therefore, the opposed mark shall be assessed in its entirety and give rise to a pronunciation of “Shangri-La-Golf” and no specific meaning.”
Based on the above finding, the Board decided the opposed mark “Shangri-La-Golf” is dissimilar to the cited mark “Shanri-La” because there is visual and phonetical distinction between the marks by virtue of the term “Golf” and the opposed mark does not give rise to a meaning related to ‘a remote usually idyllic hideaway’.
Accordingly, the Board found the opposition baseless and decided the opposed mark remains as the status quo.