In a dispute of registrability to a unique
three-dimensional shape of giant cotton candy, the Appeal Board of Japan Patent
Office (JPO) refused protection of the 3D mark due to lack of distinctiveness.
[Appeal case no. 2017-9666, Gazette issue date: September 27, 2019]
TOTTI CANDY FACTORY
If you ever visit Harajuku (Tokyo) chances are you will spot people carrying around gigantic pastel-colored cotton candy. When you think of cotton candy, a balloon-size blob of sticky blue or pink fluff probably comes to mind. But this cotton candy is here to rewrite any preconceptions you have about the treat, because not only does it come in the most beautiful shades of pastel you’ve ever seen, it’s also legitimately larger than your head. It’s so big, it’s actually hard to take a cute picture holding it — because it blocks your entire face with its pretty rainbow hues.
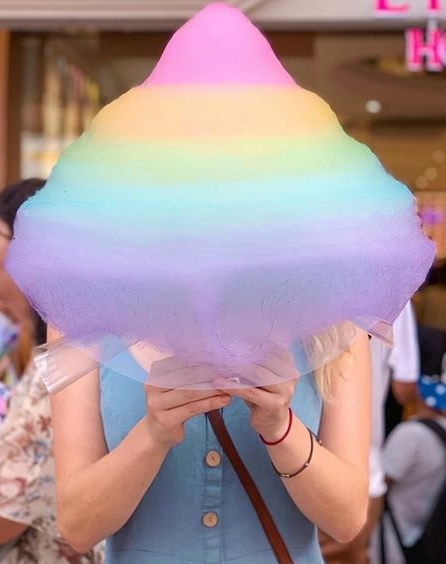

You can find this giant rainbow cotton candy at a sweet shop popular with young people in Harajuku, Totti Candy Factory.
3D shape of the cotton candy was applied
for registration with JPO in respect of confectionery (class 30) on May 20,
2016. [TM application no. 2016-54840]
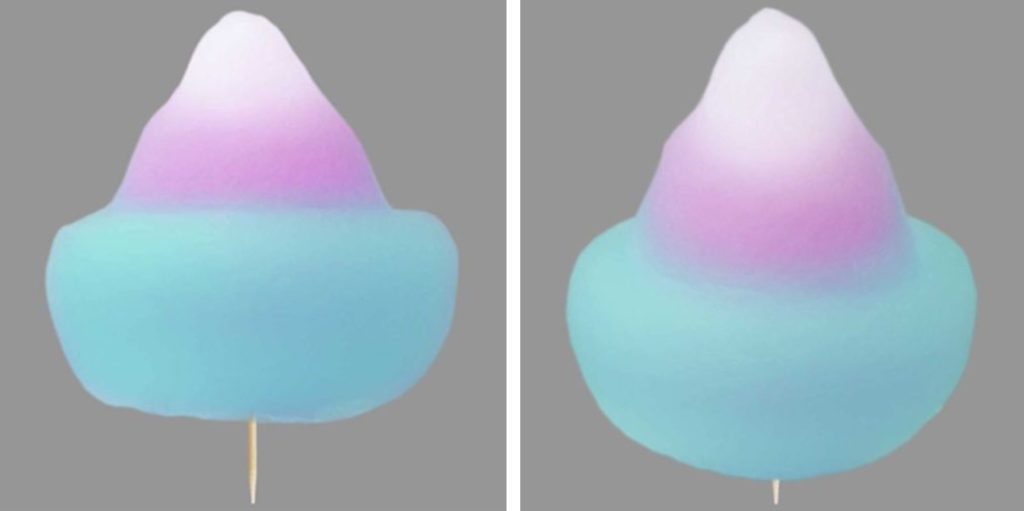

Registrability of 3D shape mark
The shape of a product can be an important element that generates value for a company. For this reason, the protection of three-dimensional forms is of commercial interest. Three-dimensional trademarks include the shape of a product or its packaging. Prior to 1996, there was no proper statutory provision that recognized three-dimensional shapes as trademarks. 1996 revision to the Trademark Law recognized 3D shape trademarks such as the shape of the packaging and specific product shapes. Now, a Trademark Registration can be attained for any distinctive three-dimensional shapes, that discern the goods or services of one business from those of other businesses, under the Japan Trademark law.
JPO Examination
JPO examiner entirely rejected the 3D shape mark by stating that:
“Appearance of the applied mark in color can be perceived merely as an ordinary three-dimensional shape of cotton candy. If so, the shape is deemed equivalent to a configuration solely consisting of the shape of goods in a common manner to the extent that relevant traders and/or consumers are unlikely to recognize the shape as a source indicator. Hence, the mark is subject to Article 3(1)(iii) of the Trademark Law. From the produced evidence, it is questionable whether the shape has acquired distinctiveness as a result of substantial use.”
Article 3(1)(iii) is a provision to prohibit any mark from registering where the mark solely consists of elements just to indicate, in a common manner, the place of origin, place of sale, quality, raw materials, efficacy, intended purpose, quantity, shape (including shape of packages), price, the method or time of production or use.
To dispute the refusal, applicant, an owner of Totti Candy Factory, filed an appeal on June 30, 2017.
Appeal Board’s decision
The Appeal Board affirmed examiner’s rejection of the 3D shape based on lack of distinctiveness. As grounds for rejection, Board cited following conical cotton candies in several colors distributed by third parties.
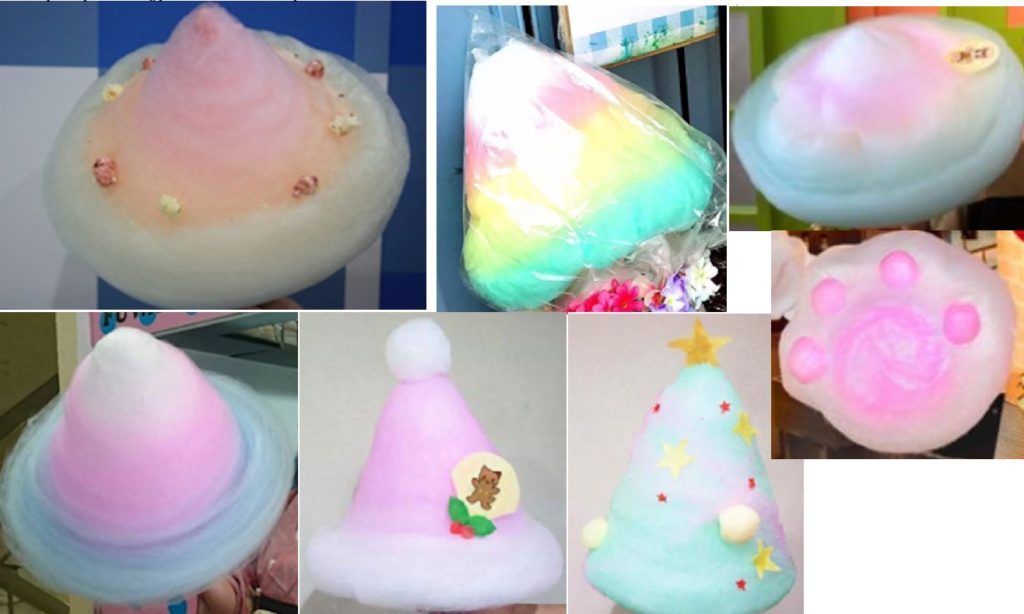

In addition, the Board negated acquired distinctiveness of the 3D shape by stating that:
- Allegedly applicant has used applied mark on cotton candy since February 2015, however, he failed to produce objective evidence of its first use.
- In general, cotton candy is consumed by individuals in a wide age range. If so, three brick-and-mortar shops at Harajuku (Tokyo), Shinsaibashi (Osaka), Nagoya PARCO (Aichi) are insufficient to demonstrate increased publicity among relevant consumers all over the country.
- According to the produced sales record, from the period of February 2015 through June 2017 applicant sold 370,302 pieces of Giant Rainbow Cotton Candy, amounting to 200 million JP-yen in total sales. However, its market share remains unclear.
- A fact that Totti Giant Cotton Candy has gotten popular with young women in their teens and early 20’s is insufficient to admit acquire distinctiveness of the 3D shape since consumers of cotton candy are not limited to young women.
- Advertisement and publications of Giant Rainbow Cotton Candy contains a term “TOTTI CANDY FACTORY” or “Totti” adjacent to the 3D shape. From these evidences, it is questionable whether relevant consumers would conceive the 3D shape in itself as a source indicator of Totti Candy Factory.
Based on the foregoing, the Board consequently refused to register the mark based on Article 3(1)(iii) of the Trademark Law.