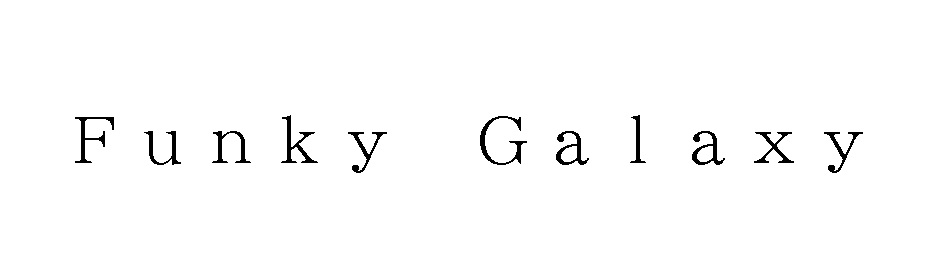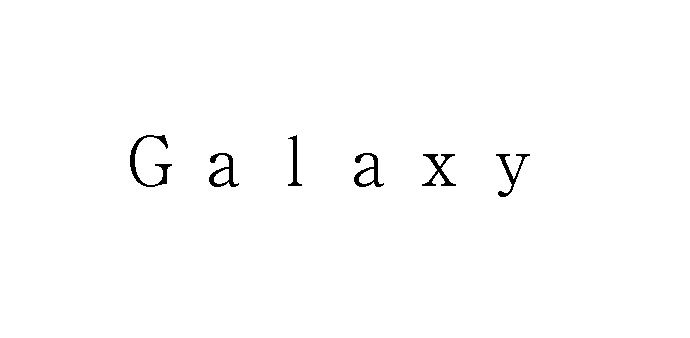The Japan Patent Office (JPO) did not side with Christian Dior Couture in a trademark opposition against TM Reg no. 6305075 for word mark “DIORLV” in class 25 by finding dissimilarity and unlikelihood of confusion with a world-renowned fashion brand “Dior”.
[Opposition case no. 2020-900352, Gazette issued date: November 26, 2021]“DIORLV”
The opposed mark, “DIORLV” in standard character, was sought for registration by a Chinese individual to be used on underwear, coats, pajamas, swimsuits, raincoats, footwear, caps and hats, gloves, trousers, skirts, yoga shirts, yoga pants in class 25 on December 25, 2019.

The JPO examiner granted protection of the opposed mark on October 13, 2020, and published for opposition on November 4, 2020.
Opposition by Christian Dior
To contend registration within a statutory period of two months counting from the publication date, Christian Dior Couture filed an opposition on December 25, 2020.
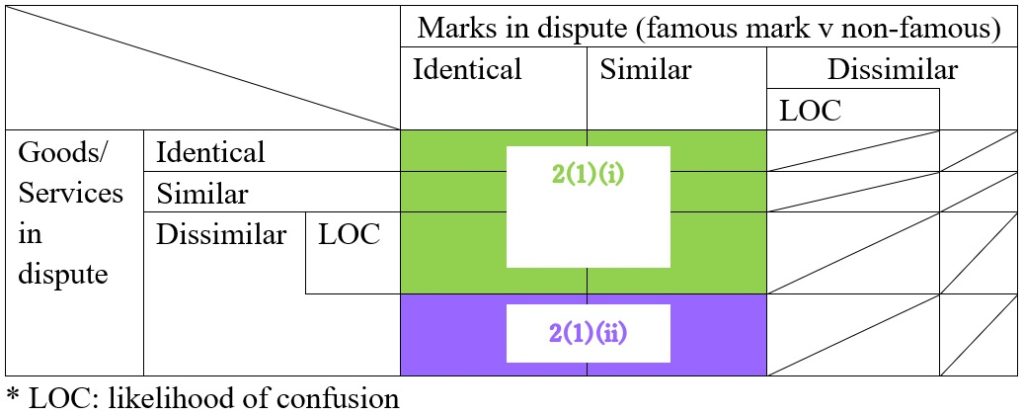
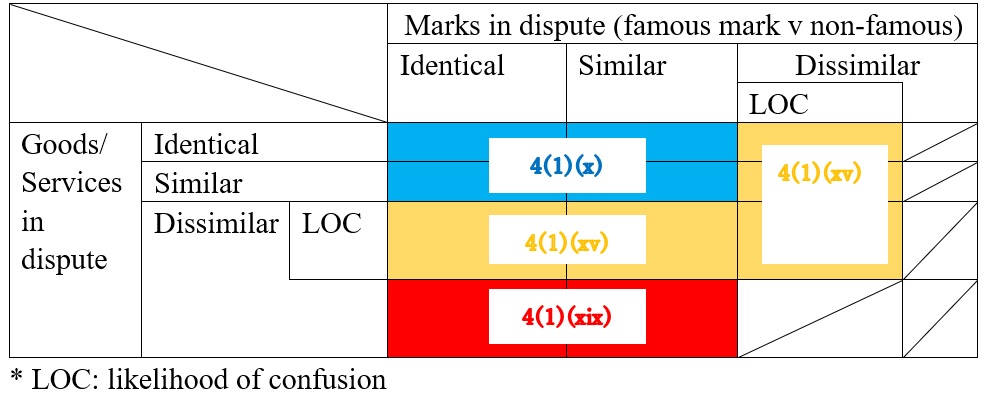
In the opposition, Christian Dior asserted the opposed mark shall be canceled in contravention of Article 4(1)(viii), (xi), (xv), (xix) of the Japan Trademark Law on the grounds that the opposed “DIORLV” mark contains the term “Dior”, an abbreviation of a world-renowned fashion brand “Christian Dior” and the opponent. Besides, the opposed mark will be perceived as a combination of abbreviation of two famous brands, “Christian Dior” and “Louis Vuitton.” If so, it is reasonable to consider the term “DIOR” as a prominent portion of the opposed mark that gives rise to the same sound and concept with the senior registered mark “Dior” owned by the opponent.
JPO decision
The Opposition Board of JPO admitted a substantial degree of reputation and popularity of “Dior” as an abbreviation of “Christian Dior” and the opponent in relation to fashion items, e.g., women’s dresses, bags, shoes, jewelry, glasses, watches, fountain pens, lighters.
In the meantime, the Board did not find the term “DIOR” as a prominent portion of the opposed mark. Based on the overall assessment of similarity, the Board held both marks dissimilarity by stating that:
- From appearance and pronunciation, “DIORLV” and “Dior” look sufficiently different with or without “LV” in the suffix position.
- Both marks are distinguishable in concept since “DIORLV” does not give rise to any specific meaning. “Dior” has a meaning of world-renowned fashion brand “Christian Dior.”
Given a low degree of similarity of the marks, it is unlikely that relevant consumers would recognize a source of goods in question bearing the opposed mark from Christian Dior Couture or any entity systematically or economically connected with the opponent.
Furthermore, the Board has no reason to believe the term “DIOR” of the opposed mark is separable from the term “LV” and independently plays a role in the source indicator. Accordingly, the opposed mark shall not be construed to contain a famous abbreviation of the opponent.
Based on the foregoing, the JPO dismissed the entire opposition and decided the opposed mark shall remain valid as the status quo.